Today’s path rounds are on 𝐑𝐡𝐨𝐝𝐨𝐜𝐨𝐜𝐜𝐮𝐬 𝐞𝐪𝐮𝐢!
𝐖𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭?
𝐑𝐡𝐨𝐝𝐨𝐜𝐨𝐜𝐜𝐮𝐬 𝐞𝐪𝐮𝐢 is a bacteria that is commonly found in the soil and in horse manure. It is considered a 𝐟𝐚𝐜𝐮𝐥𝐭𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐯𝐞 𝐢𝐧𝐭𝐫𝐚𝐜𝐞𝐥𝐥𝐮𝐥𝐚𝐫 pathogen, meaning it needs to invade into host cells in order to survive.
𝐖𝐡𝐨 𝐠𝐞𝐭𝐬 𝐢𝐭?
This disease primarily affects horses, particularly 1-6 month old foals.
𝐖𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐜𝐚𝐮𝐬𝐞𝐬 𝐢𝐭?
As mentioned before, R. equi is a soil borne bacteria, so typically foals acquire the disease from inhaling dust or ingesting dirt particles. Once the bacteria is within the foal, it gets engulfed by 𝐦𝐚𝐜𝐫𝐨𝐩𝐡𝐚𝐠𝐞𝐬 (the body’s major clean up cell). Normally when a macrophage eats a bacteria, the bacteria is enclosed in a storage unit called a 𝐩𝐡𝐚𝐠𝐨𝐬𝐨𝐦𝐞, which will fuse with a 𝐥𝐲𝐬𝐨𝐬𝐨𝐦𝐞 that contains a large number of toxic enzymes that destroy the bacteria. In the case of R. equi, however, the bacteria expresses a protein that prevents the lysosome from fusing with the phagosome, thus preventing the bacteria from getting destroyed. Crazy!
𝐖𝐡𝐲 𝐢𝐬 𝐭𝐡𝐢𝐬 𝐚 𝐩𝐫𝐨𝐛𝐥𝐞𝐦?
Because R. equi survives within macrophages, the body can’t use that mechanism in order to kill the bacteria. Therefore, it has to use a different aspect of the immune system. In order to kill the bacteria, the body must now target the infected macrophages and destroy them. So, it employs a different type of cell called 𝐤𝐢𝐥𝐥𝐞𝐫 𝐓 𝐜𝐞𝐥𝐥𝐬, which identify infected macrophages and cause them to disintegrate.
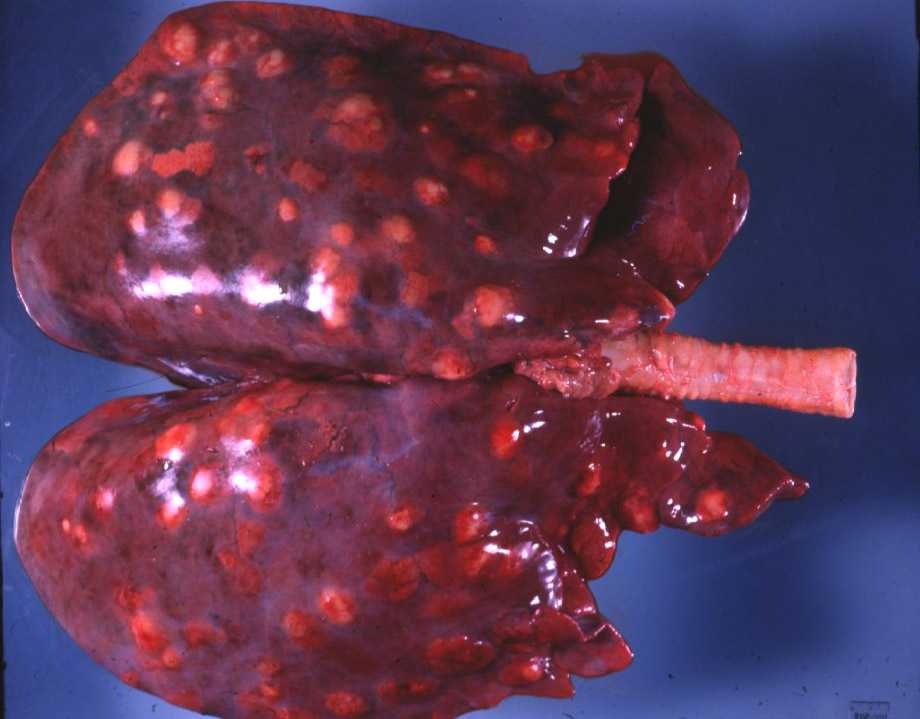
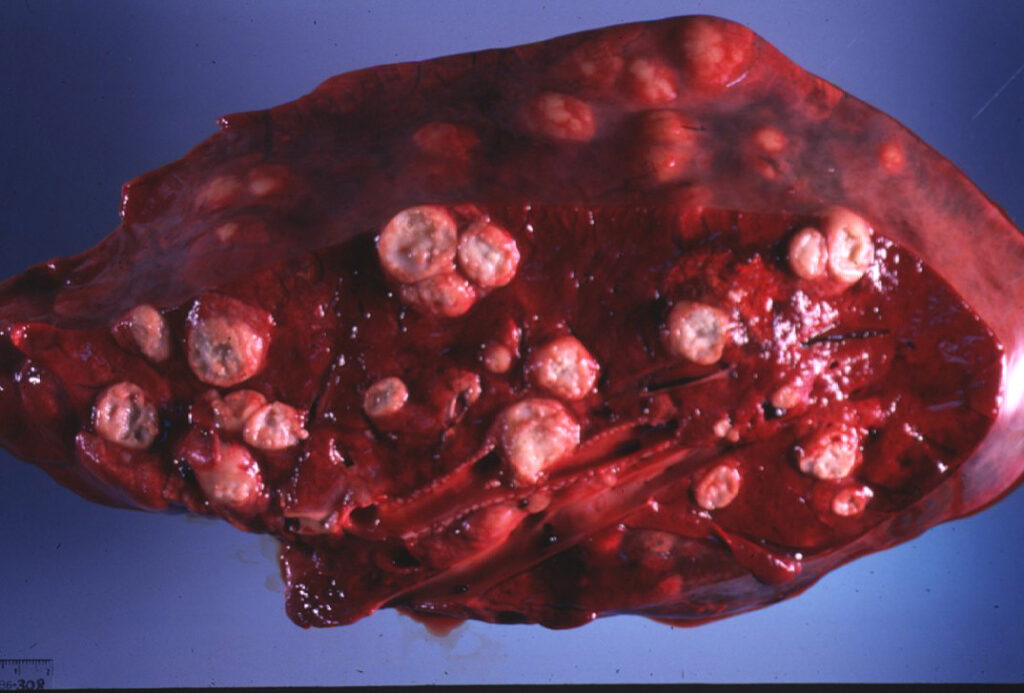
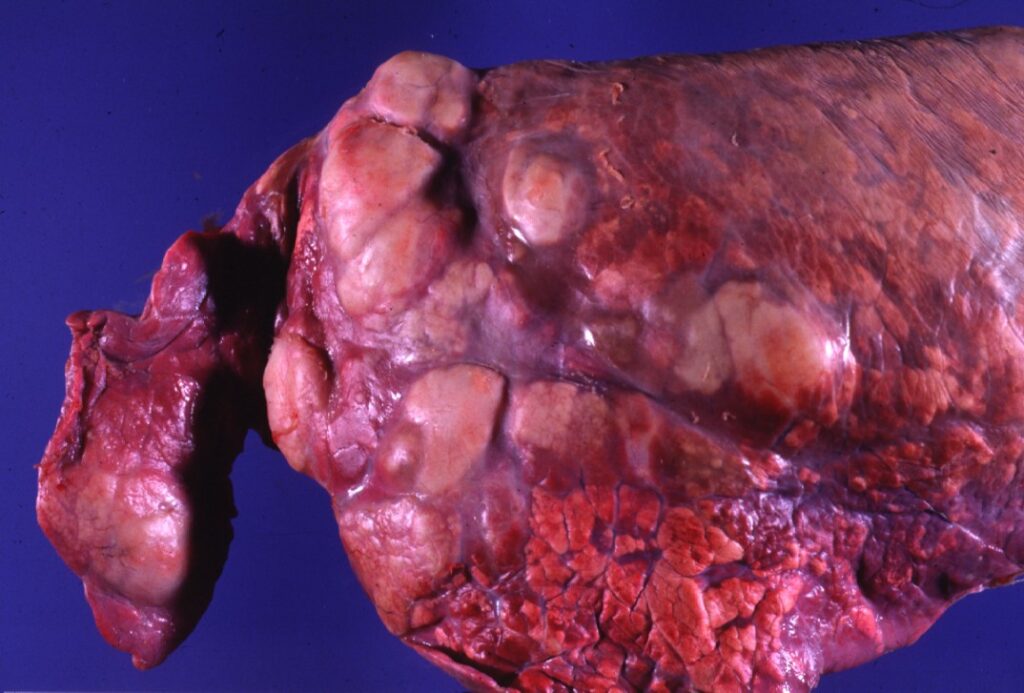
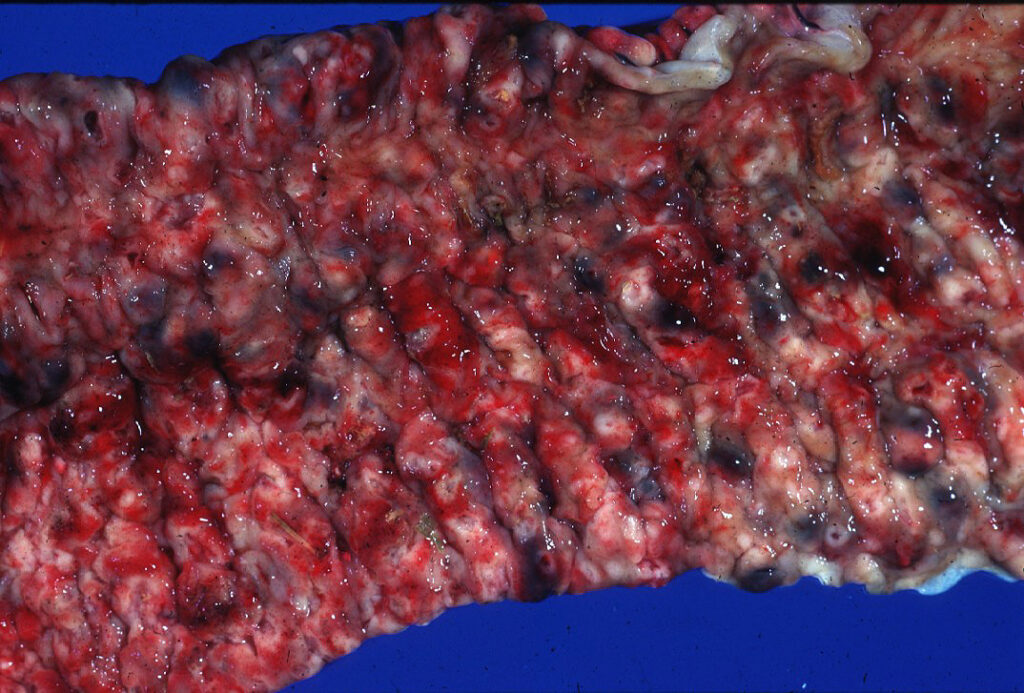
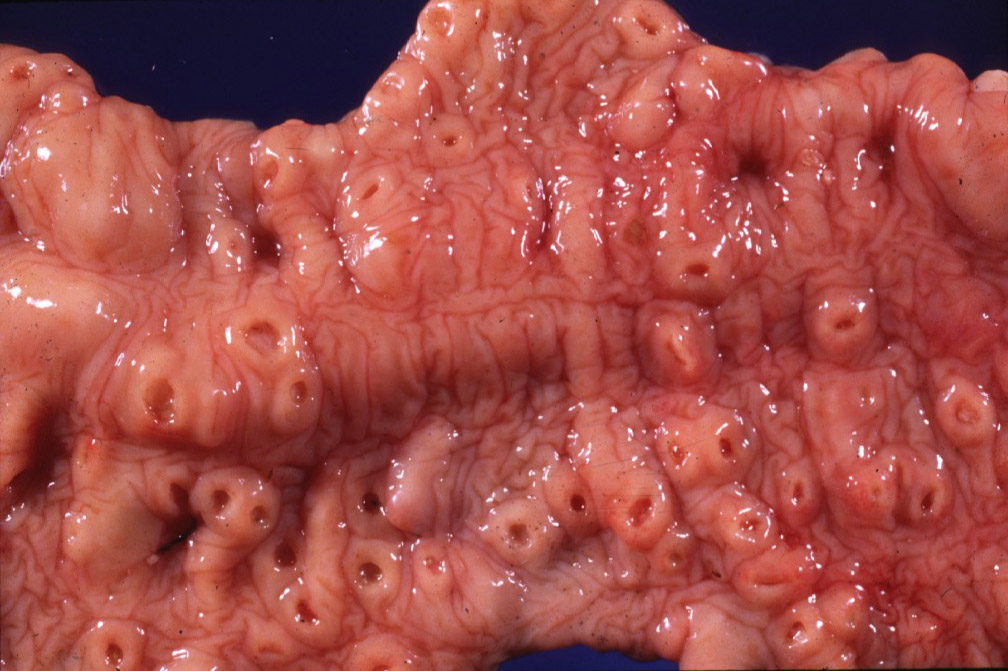
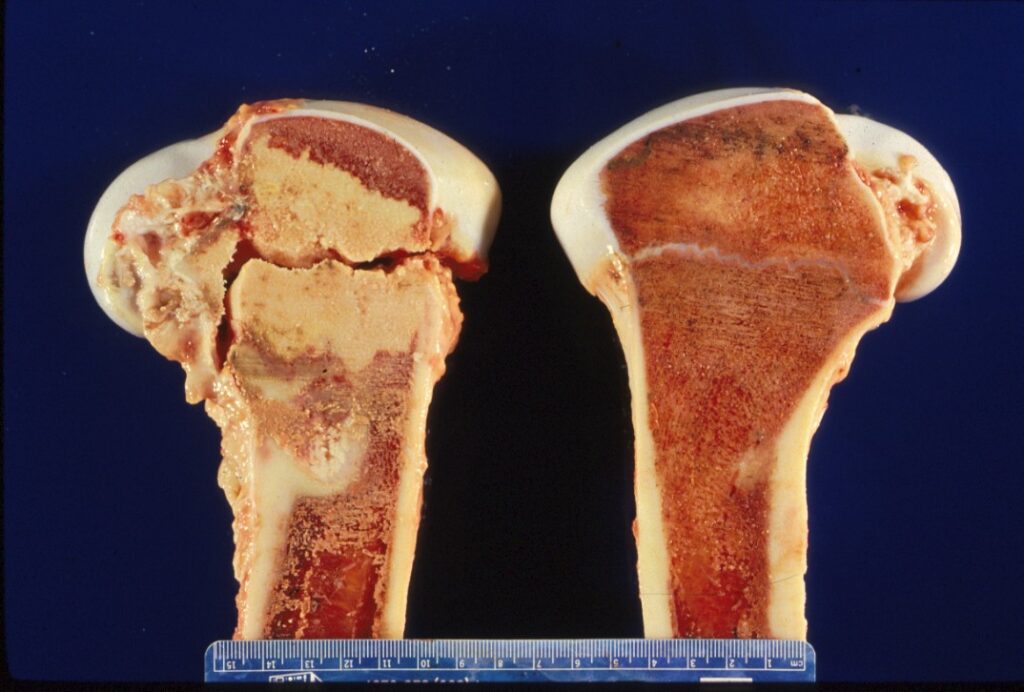
However, this type of immune activity produces a lot of inflammation! Typically, areas where the macrophages are being destroyed form 𝐚𝐛𝐬𝐜𝐞𝐬𝐬𝐞𝐬, which is basically a soupy collection of immune cells in various stages of life and death. These abscesses are generally found in the lungs, intestine and occasionally in the growth plates of bones. Ultimately, this is what causes problems for the foal, by inciting a high fever, reducing lung capacity, causing gastrointestinal issues and generally making them feel pretty dumpy.
𝐇𝐨𝐰 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭 𝐝𝐢𝐚𝐠𝐧𝐨𝐬𝐞𝐝?
This disease should be suspected any time you have a sick foal with high fever and breathing issues. From that initial suspicion, a veterinarian might do an ultrasound or take an X-ray of the chest in order to visualize the abscesses. If the disease is in the intestine or bones, similar diagnostics can be used.
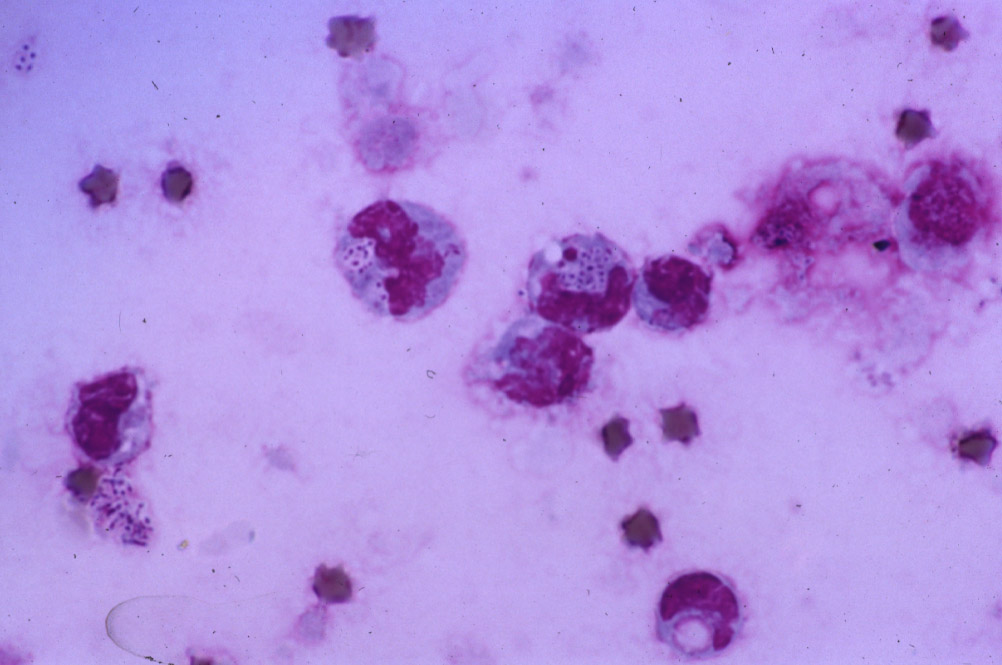
To definitively diagnose the disease, the veterinarian may do a 𝐭𝐫𝐚𝐧𝐬𝐭𝐫𝐚𝐜𝐡𝐞𝐚𝐥 𝐰𝐚𝐬𝐡, which is where they introduce sterile water into the lungs, then retrieve it to see what cells are hanging out in the lungs. When you look at the cells under a microscope, you can often see macrophages containing tiny dit dot bacteria, which is the Rhodococcus itself!
𝐇𝐨𝐰 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭 𝐭𝐫𝐞𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐝? 𝐇𝐨𝐰 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭 𝐩𝐫𝐞𝐯𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐞𝐝?
This disease requires intensive antibiotic treatment, because it is incredibly difficult for antibiotics to enter abscesses in order to do their job. However, most foals do recover from this disease and go on to live productive horsey lives! To prevent it, foals should be kept in well-ventilated, dust free areas and should be monitored closely for any signs of fever or respiratory issues.
𝐏𝐡𝐨𝐭𝐨𝐬
1) An example of what you might see after a transtracheal wash. See all the little purple dots in the cell? Those are the bacteria!
2-4) Examples of abscesses in the lungs from R. equi.
5-6) Examples of abscesses in the intestine from R. equi.
7) A growth plate infected with R. equi, forming a large abscess within the bone! Ouch.
𝐒𝐨𝐮𝐫𝐜𝐞𝐬
Maxie, G. Jubb, Kennedy and Palmer’s Pathology of Domestic Animals, Volume 2. Sixth Edition.
Rush, BR. Rhodococcus equi Pneumonia in foals. Merck Vet Manual 2014.
Photos 1-7 courtesy of Noah’s Arkive.