


Today’s path rounds are on 𝐡𝐢𝐩 𝐝𝐲𝐬𝐩𝐥𝐚𝐬𝐢𝐚!
𝐖𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭?
𝐇𝐢𝐩 𝐝𝐲𝐬𝐩𝐥𝐚𝐬𝐢𝐚 is an extremely common condition in large and giant breed dogs, and results in 𝐥𝐚𝐱𝐢𝐭𝐲 (looseness) of the hip joints.
𝐖𝐡𝐨 𝐠𝐞𝐭𝐬 𝐢𝐭?
As mentioned, we most commonly see this condition in large and giant breed dogs. Typically, this disease first begins to cause issues around 1 year of age.
𝐖𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐜𝐚𝐮𝐬𝐞𝐬 𝐢𝐭?
Hip dysplasia is considered to have a 𝐦𝐮𝐥𝐭𝐢𝐟𝐚𝐜𝐭𝐨𝐫𝐢𝐚𝐥 𝐩𝐚𝐭𝐡𝐨𝐠𝐞𝐧𝐞𝐬𝐢𝐬, meaning it occurs based on the interplay of several different factors. In general, the disease is considered to be 𝐢𝐧𝐡𝐞𝐫𝐢𝐭𝐞𝐝, with the severity of the disease being modified by different environmental factors as the puppy grows. Known contributing factors to this disease include excessive growth, increased exercise and nutritional imbalances.
𝐖𝐡𝐲 𝐢𝐬 𝐭𝐡𝐢𝐬 𝐚 𝐩𝐫𝐨𝐛𝐥𝐞𝐦?
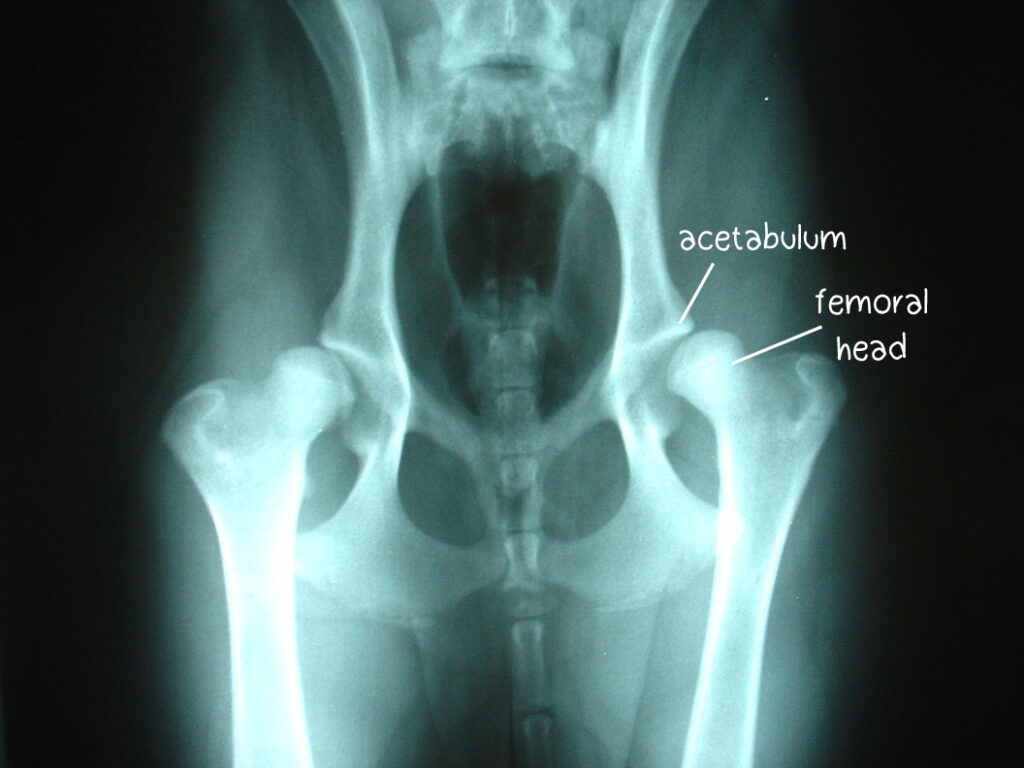
The exact biomechanical cause of hip dysplasia varies between animals, however the ultimate result is joint laxity. Typically, this laxity is due to a flattened 𝐚𝐜𝐞𝐭𝐚𝐛𝐮𝐥𝐮𝐦 (the divot in the pelvis) that is inadequately covering the 𝐟𝐞𝐦𝐨𝐫𝐚𝐥 𝐡𝐞𝐚𝐝 (the part of the femur that fits into the pelvis). Over time, the body responds to the joint laxity by depositing new bone in the area, in a desperate attempt to try and stabilize the joint. This causes 𝐝𝐞𝐠𝐞𝐧𝐞𝐫𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐯𝐞 𝐣𝐨𝐢𝐧𝐭 𝐝𝐢𝐬𝐞𝐚𝐬𝐞, where the joint is on a slippery slope to developing severe arthritis that is extremely painful for the animal. Ultimately, this causes lameness and pain during motion of the joint.
𝐇𝐨𝐰 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭 𝐝𝐢𝐚𝐠𝐧𝐨𝐬𝐞𝐝?
X-rays are the standard for diagnosis, as it allows for evaluation of the bony structures and any new bone that has been deposited. Standardized X-ray procedures can be used to identify puppies at risk of developing hip dysplasia, by looking at the degree of coverage of the acetabulum around the femoral head.
𝐇𝐨𝐰 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭 𝐭𝐫𝐞𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐝?
There are two main treatment options: medical and surgical. For dogs with less severe lameness, medical management can be successful. Usually this involves long term pain control, weight loss and physiotherapy. For more severe cases, surgical options are available, including 𝐭𝐨𝐭𝐚𝐥 𝐡𝐢𝐩 𝐫𝐞𝐩𝐥𝐚𝐜𝐞𝐦𝐞𝐧𝐭.
𝐏𝐡𝐨𝐭𝐨𝐬
1) An X-ray of a young puppy with hip dysplasia. Notice how the acetabulum doesn’t cover the head of the femur very well!
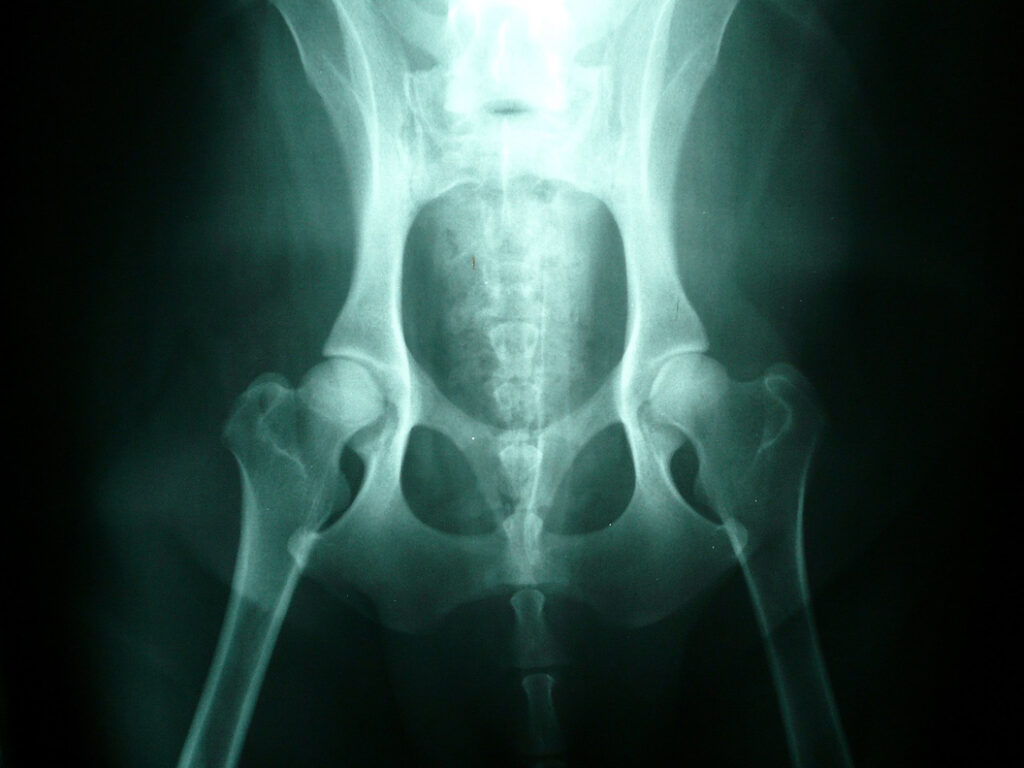
2) An older dog who has developed arthritis from hip dysplasia. Note the bony proliferation!
3) A dog with a total hip replacement, shown on the right. You can also see signs of arthritis in the hip on the left.
4) A normal dog to compare with the other X-rays!
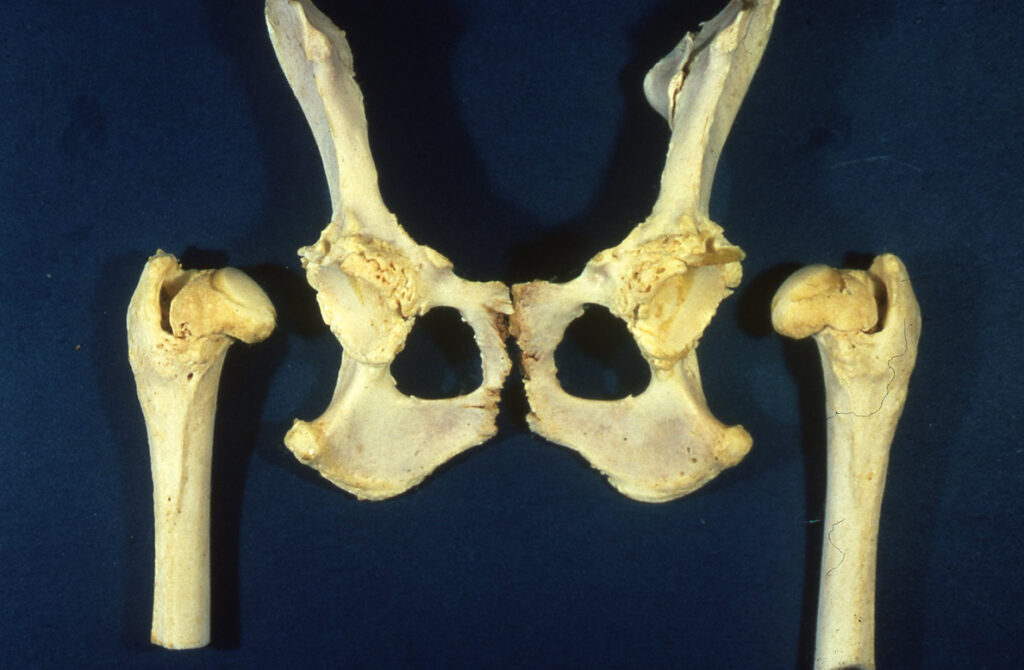
5-6) Examples of what that bony proliferation looks like at necropsy.
𝐒𝐨𝐮𝐫𝐜𝐞𝐬
Maxie, G. Jubb, Kennedy and Palmer’s Pathology of Domestic Animals, Volume 1. Sixth Edition.
Harari J. Hip Dysplasia in Dogs. Merck Veterinary Manual, 2022.
Photos 1-4 © Wikimedia Commons contributor Joelmills licensed under CC 3.0 International.
Photos 5-6 © Noah’s Arkive contributors Ward, Jakowski licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0.