

Today’s path rounds are on 𝐟𝐨𝐨𝐭 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐦𝐨𝐮𝐭𝐡 𝐝𝐢𝐬𝐞𝐚𝐬𝐞!
𝐖𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭?
𝐅𝐨𝐨𝐭 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐦𝐨𝐮𝐭𝐡 𝐝𝐢𝐬𝐞𝐚𝐬𝐞 (FMD) is a viral disease of significant economic importance in food production species. Outbreaks of this disease can have disastrous consequences for agriculture, such as the 2001 outbreak in the United Kingdom that was estimated to cost £𝟖 𝐛𝐢𝐥𝐥𝐢𝐨𝐧 and resulted in the destruction of more than 𝟔 𝐦𝐢𝐥𝐥𝐢𝐨𝐧 sheep and cattle.
𝐖𝐡𝐨 𝐠𝐞𝐭𝐬 𝐢𝐭?
We this condition in 𝐜𝐥𝐨𝐯𝐞𝐧-𝐡𝐨𝐨𝐯𝐞𝐝 𝐬𝐩𝐞𝐜𝐢𝐞𝐬, or species with two toes on each foot! This includes sheep, cattle, pigs and wildlife species.
𝐖𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐜𝐚𝐮𝐬𝐞𝐬 𝐢𝐭?
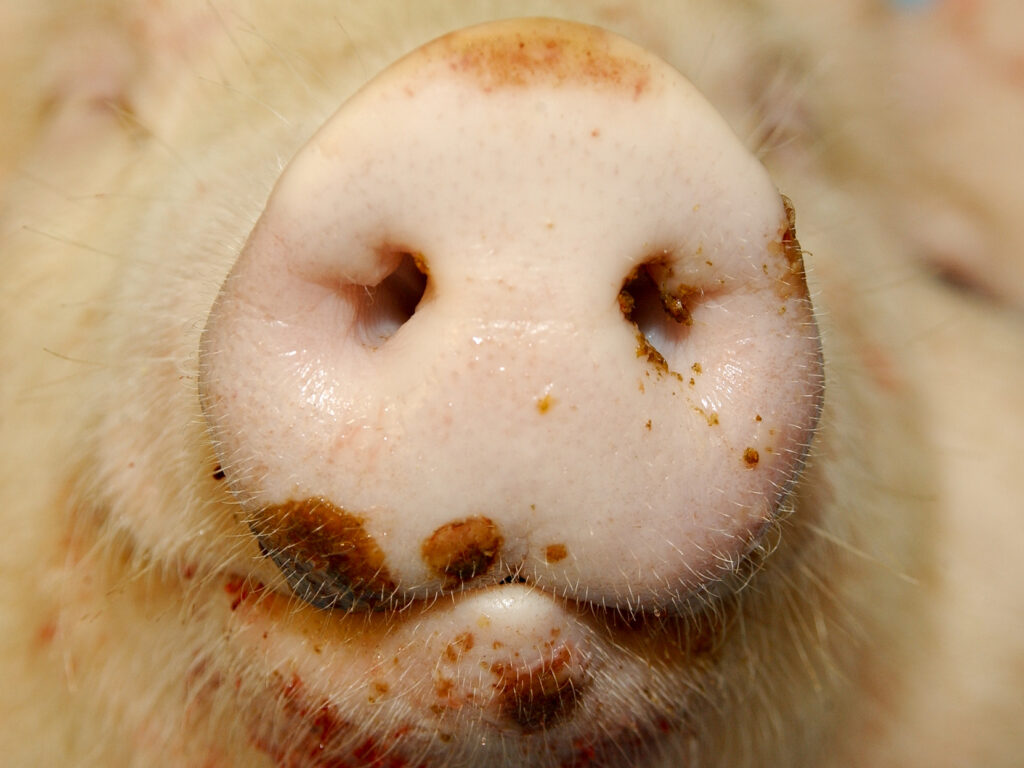
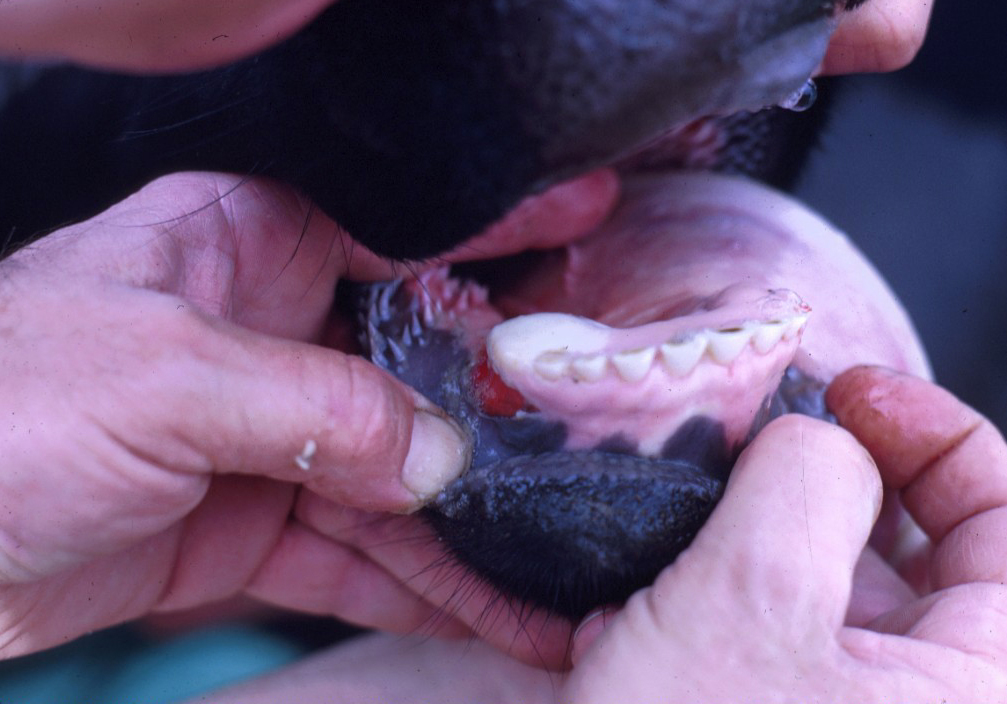
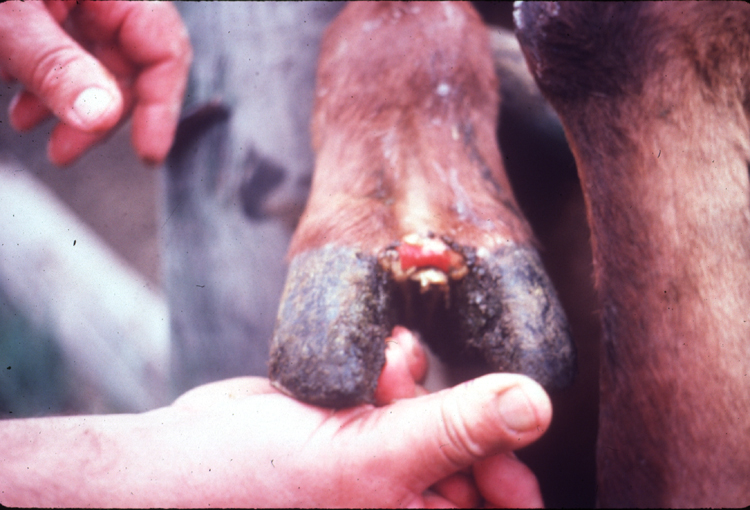
Foot and mouth disease is caused by a 𝐩𝐢𝐜𝐨𝐫𝐧𝐚𝐯𝐢𝐫𝐮𝐬, which is transmitted by direct contact with an infected animal or contacting that animal’s secreted fluids, like saliva or milk. The virus enters the body primarily through inhalation or ingestion, where it replicates in the 𝐩𝐡𝐚𝐫𝐲𝐧𝐱 (throat). Here it accesses the 𝐥𝐲𝐦𝐩𝐡𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐜 𝐬𝐲𝐬𝐭𝐞𝐦 (draining vessels) and spreads throughout the body. The virus characteristically produces 𝐯𝐞𝐬𝐢𝐜𝐥𝐞𝐬, which are basically blisters on the skin surface. These vesicles most commonly occur around the hooves and in the mouth.
𝐖𝐡𝐲 𝐢𝐬 𝐭𝐡𝐢𝐬 𝐚 𝐩𝐫𝐨𝐛𝐥𝐞𝐦?
The vesicles formed by the virus are quite painful, and can cause lameness and 𝐝𝐲𝐬𝐩𝐡𝐚𝐠𝐢𝐚 (difficulty eating). The virus also causes a high fever. Young animals are most severely affected due to damage to their heart, causing sudden death. However, the real problem with FMD is how infective it is! The virus can be spread by clothes, vehicles, equipment, feed or even wildlife moving between farms, which is why it is so costly to contain outbreaks.
𝐇𝐨𝐰 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭 𝐝𝐢𝐚𝐠𝐧𝐨𝐬𝐞𝐝?
Diagnosis is made using a 𝐏𝐂𝐑 𝐭𝐞𝐬𝐭, which detects the genes of the virus directly.
𝐇𝐨𝐰 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭 𝐭𝐫𝐞𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐝? 𝐇𝐨𝐰 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭 𝐩𝐫𝐞𝐯𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐞𝐝?
Most countries do not allow treatment of affected animals, as they are too risky to keep around to potentially infect others. Cattle that survive the infection can continue to carry the virus for up to 3.5 years! So, most countries focus on prevention through culling all animals on infected farms, restricting and tracing animal movements, and testing all animals imported into the country.
𝐏𝐡𝐨𝐭𝐨𝐬
1-5) The characteristic blisters of FMD in the mouth and around the hooves!
𝐒𝐨𝐮𝐫𝐜𝐞𝐬
Maxie, G. Jubb, Kennedy and Palmer’s Pathology of Domestic Animals, Volume 2. Sixth Edition.
Belsham GJ, Botner A, Lohse L. Foot-and-mouth disease in animals. Merck Veterinary Manual 2021.
Photos 1-5 © Noah’s Arkive contributors Adsit, Dark, King licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0.