Today’s path rounds are on 𝐉𝐨𝐡𝐧𝐞’𝐬 𝐝𝐢𝐬𝐞𝐚𝐬𝐞, otherwise known as paratuberculosis!
𝐖𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭?
𝐉𝐨𝐡𝐧𝐞’𝐬 𝐝𝐢𝐬𝐞𝐚𝐬𝐞 is a bacterial disease of ruminants that primarily affects the intestinal tract. It is a huge source of production loss, particularly for dairy cattle, so it is a very important disease!
𝐖𝐡𝐨 𝐠𝐞𝐭𝐬 𝐢𝐭?
This disease is most common in domestic ruminants, like sheep, cattle and goats. However, it can also occur in other species. Interestingly, it only seems to affect older animals, due to a long 𝐬𝐮𝐛𝐜𝐥𝐢𝐧𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐥 𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐢𝐨𝐝 where the animal shows no clinical signs, despite being infected.
𝐖𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐜𝐚𝐮𝐬𝐞𝐬 𝐢𝐭?
Johne’s is caused by 𝐌𝐲𝐜𝐨𝐛𝐚𝐜𝐭𝐞𝐫𝐢𝐮𝐦 𝐚𝐯𝐢𝐮𝐦 𝐩𝐚𝐫𝐚𝐭𝐮𝐛𝐞𝐫𝐜𝐮𝐥𝐨𝐬𝐢𝐬 (MAP). This bacteria is primarily transmitted through fecal contamination of feed, but can also be transmitted in milk or water.
Once in the intestinal tract, the bacteria invades the cells lining the small intestine, and is taken up by 𝐦𝐚𝐜𝐫𝐨𝐩𝐡𝐚𝐠𝐞𝐬 (the body’s main clean-up cell) into a 𝐩𝐡𝐚𝐠𝐨𝐬𝐨𝐦𝐞 (a storage bag within a macrophage). Normally, things ingested by macrophages are broken down quickly by 𝐥𝐲𝐬𝐨𝐬𝐨𝐦𝐞𝐬 (big bags of enzymes that fuse with the phagosome). However, MAP is able to prevent fusion of lysosomes to phagosomes, allowing it to survive within the macrophage.
The bacteria will live happily in these macrophages for up to 2-5 years, with the animal constantly shedding low levels of bacteria in the feces that can infect other animals. After a long period of time, the body’s immune system finally takes notice, and begins a rapid, but not very effective, immune response against the bacteria, leading to clinical signs for the affected animal.
𝐖𝐡𝐲 𝐢𝐬 𝐭𝐡𝐢𝐬 𝐚 𝐩𝐫𝐨𝐛𝐥𝐞𝐦?
Once the immune system has kicked in, a 𝐠𝐫𝐚𝐧𝐮𝐥𝐨𝐦𝐚𝐭𝐨𝐮𝐬 𝐫𝐞𝐬𝐩𝐨𝐧𝐬𝐞, accumulation of large numbers of macrophages, occurs in the intestine and nearby lymph nodes. This accumulation leads to thickening of the intestinal mucosa, which prevents proper absorption of nutrients and water from the intestinal tract. As a result, these animals develop diarrhea and severe weight loss, because they can’t get any of the nutrients they need to survive. Eventually these animals will die.
𝐇𝐨𝐰 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭 𝐝𝐢𝐚𝐠𝐧𝐨𝐬𝐞𝐝?
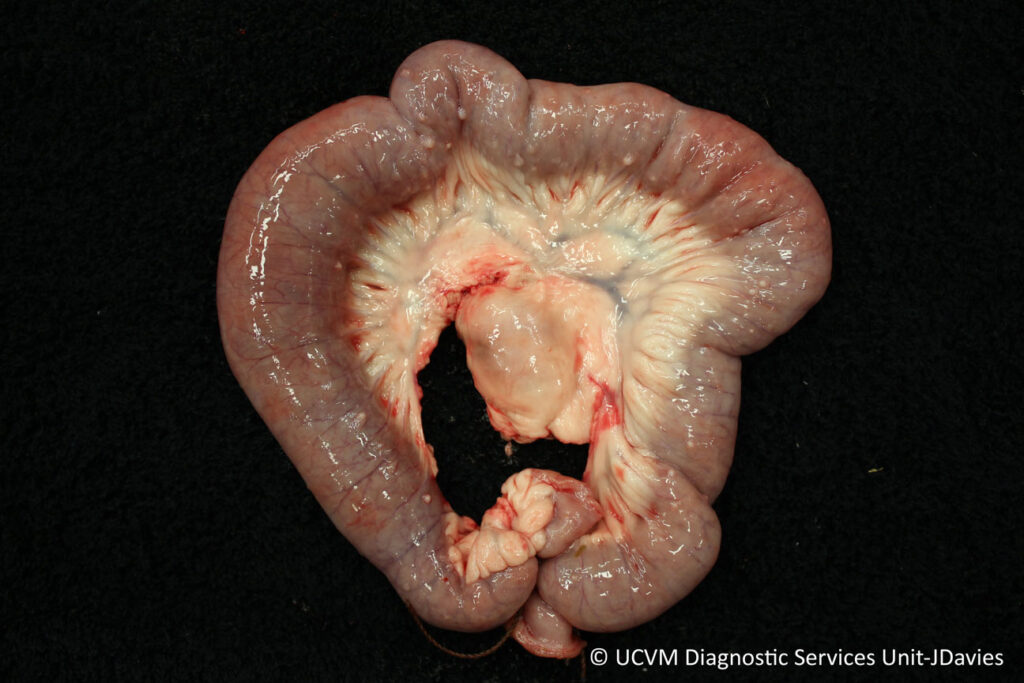
Usually this disease is diagnosed based on clinical suspicion, as it is one of the main causes of diarrhea and weight loss in an older ruminant. However, if a clinician wants to confirm their diagnosis, they can run a culture or PCR test on the feces to detect the bacteria. At necropsy, the classic lesion is thickening of the intestinal mucosa, which produces thick folds along the inner intestinal surface. Often, you can also see 𝐥𝐲𝐦𝐩𝐡𝐚𝐧𝐠𝐢𝐭𝐢𝐬 (swelling of the lymphatics) in the lymph vessels of the 𝐦𝐞𝐬𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐞𝐫𝐲 (the connective tissue that holds the intestines together).
𝐇𝐨𝐰 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭 𝐭𝐫𝐞𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐝?
Unfortunately, there is no treatment for clinical Johne’s disease. Prevention is the key to management. Animals should be tested before being introduced to a herd, and young animals should be kept in clean environments with minimal exposure to older animals.
𝐏𝐡𝐨𝐭𝐨𝐬
1) A segment of thickened intestine due to Johne’s disease.
2) The classic appearance of thickened intestinal mucosa forming folds.
3) Dilated lymphatics due to Johne’s disease.
𝐒𝐨𝐮𝐫𝐜𝐞𝐬
Maxie, G. Jubb, Kennedy and Palmer’s Pathology of Domestic Animals, Volume 2. Sixth Edition.
Photos 1-3 courtesy of University of Calgary Diagnostic Services Unit.