Today’s path rounds are on 𝐭𝐫𝐚𝐧𝐬𝐦𝐢𝐬𝐬𝐢𝐛𝐥𝐞 𝐯𝐞𝐧𝐞𝐫𝐞𝐚𝐥 𝐭𝐮𝐦𝐨𝐮𝐫𝐬!
𝐖𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭?
𝐓𝐫𝐚𝐧𝐬𝐦𝐢𝐬𝐬𝐢𝐛𝐥𝐞 𝐯𝐞𝐧𝐞𝐫𝐞𝐚𝐥 𝐭𝐮𝐦𝐨𝐮𝐫𝐬 (TVTs) are one of the few known types of tumour that can be spread by contact, like an infectious disease. This is an extremely rare feature for a tumour to have!
𝐖𝐡𝐨 𝐠𝐞𝐭𝐬 𝐢𝐭?
Dogs get this tumour.
𝐖𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐜𝐚𝐮𝐬𝐞𝐬 𝐢𝐭?
As mentioned, this tumour is spread from dog to dog, typically during coitus.
This tumour has a particularly unique behaviour, even among infectious tumours. TVTs are actually a 𝐱𝐞𝐧𝐨𝐠𝐫𝐚𝐟𝐭, meaning a graft of tissue from another species. Genetic evaluation of the tumour cells revealed that these cells actually contain 𝟓𝟗 𝐜𝐡𝐫𝐨𝐦𝐨𝐬𝐨𝐦𝐞𝐬, rather than the typical 78 chromosomes that dogs have.
Further research showed that the genetic composition of these 59 chromosomes is most similar to wolf DNA… wolves that lived about 𝟏𝟏 𝟎𝟎𝟎 𝐲𝐞𝐚𝐫𝐬 𝐚𝐠𝐨, that is! This means that this tumour has essentially been “living” as its own type of pathogen since it was originally spread from ancient canid populations to domestic dog species.
𝐖𝐡𝐲 𝐢𝐬 𝐭𝐡𝐢𝐬 𝐚 𝐩𝐫𝐨𝐛𝐥𝐞𝐦?
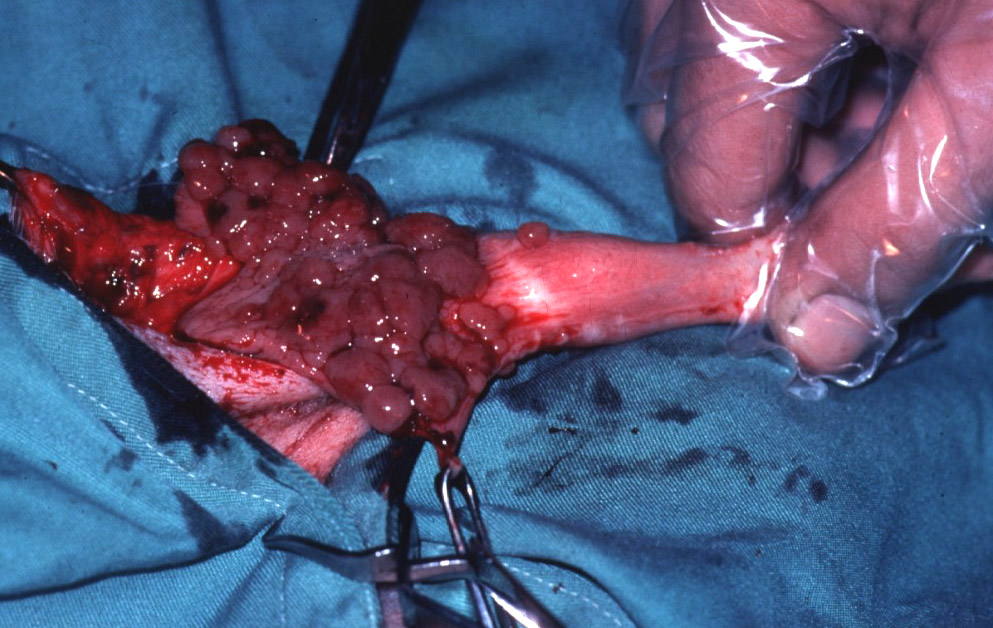
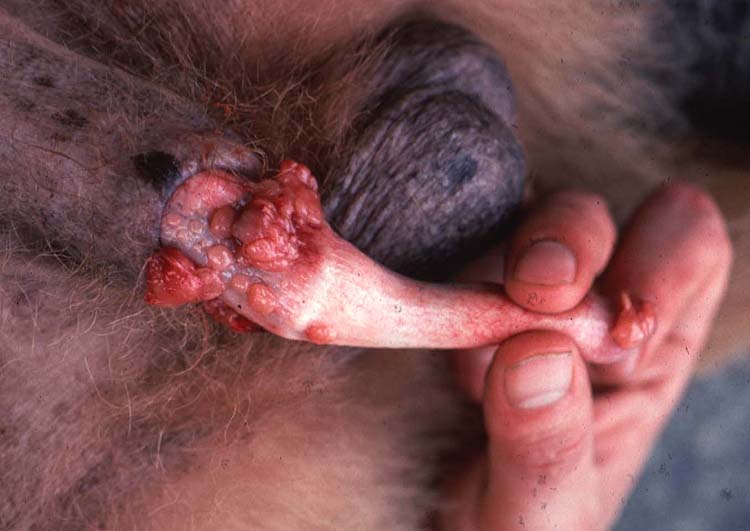
This tumour typically occurs on the genitalia, where it grows rapidly and is susceptible to bleeding. This usually doesn’t bother the animal’s day to day life too much, but urination may become painful for these animals.
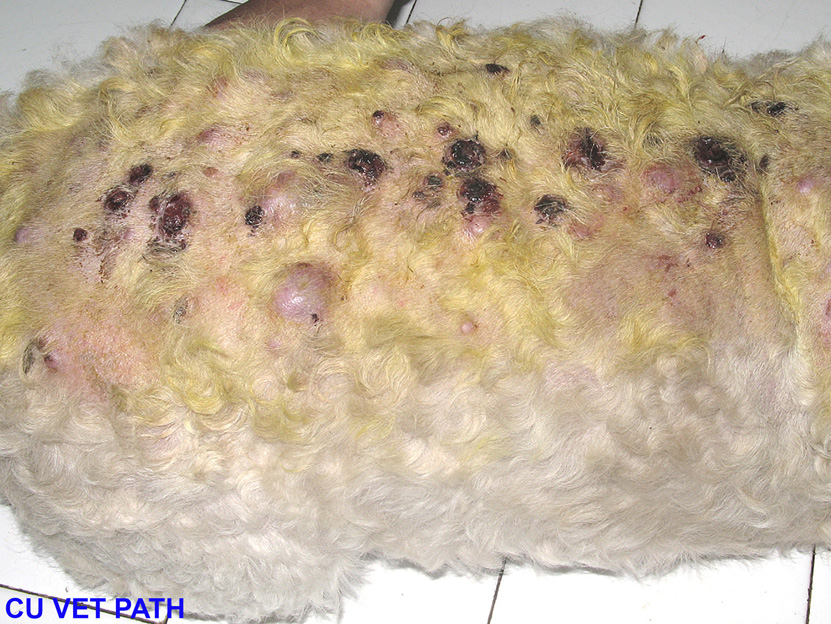
More problematic is when the tumour accidentally becomes implanted somewhere else on the dog. Common areas are the skin, mouth or nose. The tumour may also metastasize to internal organs, including the brain. These metastases can cause a wide range of effects depending on the tissue involved!
𝐇𝐨𝐰 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭 𝐝𝐢𝐚𝐠𝐧𝐨𝐬𝐞𝐝?
TVTs can be diagnosed by a 𝐟𝐢𝐧𝐞 𝐧𝐞𝐞𝐝𝐥𝐞 𝐚𝐬𝐩𝐢𝐫𝐚𝐭𝐞, where a needle is used to sample the cells to look at them under the microscope. They can also be diagnosed on a biopsy.
𝐇𝐨𝐰 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭 𝐭𝐫𝐞𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐝?
TVTs are typically treated with chemotherapy or radiation therapy. These tumours typically have a good prognosis, unless metastases are involved.
𝐏𝐡𝐨𝐭𝐨𝐬
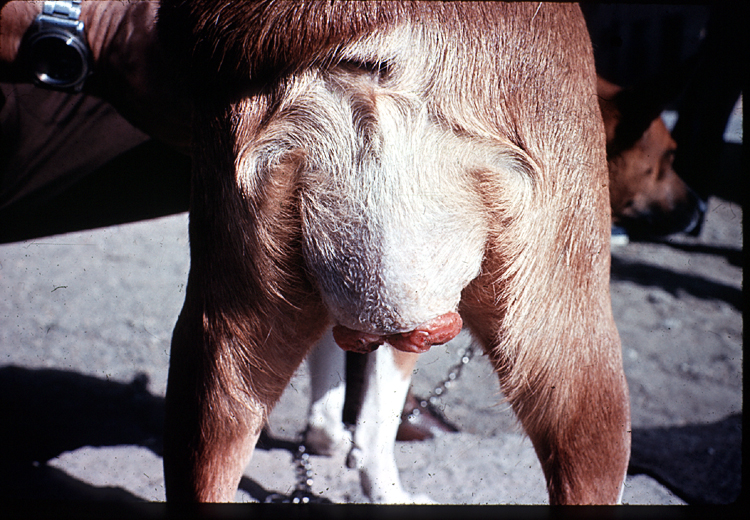
1-3) Examples of TVT on the penis of dogs.
4) TVT enlarging the vulva.
5) An example of TVT on the skin.
6) An example of TVT on the tissues around the eye! Poor pup ![]()
𝐒𝐨𝐮𝐫𝐜𝐞𝐬
Maxie, G. Jubb, Kennedy and Palmer’s Pathology of Domestic Animals, Volume 3. Sixth Edition.
Kutzler M. Canine transmissible venereal tumour. Merck Veterinary Manual 2020.
Photos 1-6 © Noah’s Arkive contributor Barretto/Araujo, Kesdangsakonwut, King, Domingo licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0.