Today’s path rounds is on 𝐩𝐮𝐥𝐦𝐨𝐧𝐚𝐫𝐲 𝐭𝐡𝐫𝐨𝐦𝐛𝐨𝐞𝐦𝐛𝐨𝐥𝐢𝐬𝐦! This topic is related to a case I had this week.
𝐖𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭?
A 𝐭𝐡𝐫𝐨𝐦𝐛𝐮𝐬 is basically a giant blood clot that completely blocks blood flow through a vessel. An 𝐞𝐦𝐛𝐨𝐥𝐮𝐬 is a more broad term, covering everything from smaller thrombi, bacteria, parasites or foreign material. Put them together, and you get 𝐭𝐡𝐫𝐨𝐦𝐛𝐨𝐞𝐦𝐛𝐨𝐥𝐢𝐬𝐦, which is a blockage of a vessel from either a thrombus or an embolus. Today, we are talking about what happens when a thrombus forms within the pulmonary veins or arteries specifically.
𝐖𝐡𝐨 𝐠𝐞𝐭𝐬 𝐢𝐭?
All species can get this!
𝐖𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐜𝐚𝐮𝐬𝐞𝐬 𝐢𝐭?
There are a lot of different potential causes of pulmonary thromboembolism, but they can be broken down into two main categories: clotting issues, and stuff that shouldn’t be there. Thrombi are essentially caused by some kind of disturbance in blood clotting. In a normal blood vessel, the body works hard to maintain a balance between 𝐜𝐨𝐚𝐠𝐮𝐥𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 (blood clotting) and 𝐟𝐢𝐛𝐫𝐢𝐧𝐨𝐥𝐲𝐬𝐢𝐬 (breaking down of blood clots). When this balance is disturbed, there are two possible outcomes. Either the blood begins to clot where it shouldn’t, forming a thrombus, or you get excessive breakdown of clots, potentially leading to the animal 𝐡𝐞𝐦𝐨𝐫𝐫𝐡𝐚𝐠𝐢𝐧𝐠 (bleeding out or losing large amounts of blood). There are way too many diseases that can disturb this balance to describe here, but that’s the gist of it!Emboli are basically big clumps of something that shouldn’t be in the blood stream. One example might be small pieces of a thrombus elsewhere in the body that have broken off, and flowed downstream to another blood vessel. Similarly, bacteria, tumour cells and parasites can form aggregates in the blood stream that can cause blockages. Even weird things like BB gun pellets, bullets, hair, cartilage or globs of fat can end up in the blood vessels and cause an embolus!
𝐖𝐡𝐲 𝐚𝐫𝐞 𝐭𝐡𝐞𝐲 𝐚 𝐩𝐫𝐨𝐛𝐥𝐞𝐦?
Most of the time a small thromboembolism isn’t really a big deal for the lungs. Each region of the lungs has a lot of 𝐜𝐨𝐥𝐥𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐫𝐚𝐥 𝐜𝐢𝐫𝐜𝐮𝐥𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧, meaning they receive blood from a lot of different places, so if one of those blood pathways is obstructed, they can make up for it by getting more blood from other sources. However, sometimes you can get large thromboemboli that obstruct an entire branch of the 𝐩𝐮𝐥𝐦𝐨𝐧𝐚𝐫𝐲 𝐚𝐫𝐭𝐞𝐫𝐲, the major blood supply to the lungs that originates in the heart. If this artery becomes completely obstructed, suddenly the blood in the right side of the heart has nowhere to go, and the left side of the heart stops getting blood back from the lungs. This leads to severe heart dysfunction, a massive drop in blood pressure, and often sudden death.
𝐖𝐡𝐲 𝐝𝐨 𝐭𝐡𝐫𝐨𝐦𝐛𝐨𝐞𝐦𝐛𝐨𝐥𝐢 𝐠𝐨 𝐭𝐨 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐥𝐮𝐧𝐠𝐬?
Realistically, thromboemboli can become lodged anywhere, however they are very frequently found in the lungs. The reason is all of the tiny vessels the lungs have. Once a thromboembolus enters the lungs, it goes through progressively smaller and smaller blood vessels, meaning that there is a high likelihood that eventually it will encounter a blood vessel it cannot squeeze through!
𝐇𝐨𝐰 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭 𝐝𝐢𝐚𝐠𝐧𝐨𝐬𝐞𝐝?
The clinical signs of pulmonary thromboembolism are pretty 𝐧𝐨𝐧-𝐬𝐩𝐞𝐜𝐢𝐟𝐢𝐜, meaning it can be hard to pin down what’s going on. Sometimes, animals will have 𝐝𝐲𝐬𝐩𝐧𝐞𝐚 (difficulty breathing), 𝐭𝐚𝐜𝐡𝐲𝐩𝐧𝐞𝐚 (increased breathing rate), coughing and lethargy. They will likely also be 𝐜𝐲𝐚𝐧𝐨𝐭𝐢𝐜 (tissues turning blue due to lack of oxygen). However, it is quite common that animals present with sudden death, without many signs leading up to the event.
𝐇𝐨𝐰 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭 𝐭𝐫𝐞𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐝?
Unfortunately in animals our treatment options are pretty limited. In humans, they will try and do open heart surgery to remove the clot, or give a whopping dose of 𝐭𝐡𝐫𝐨𝐦𝐛𝐨𝐥𝐲𝐭𝐢𝐜𝐬, drugs that are used to break down clots. Both of these treatments are quite risky, and overall the condition has a very high fatality rate.
𝐏𝐡𝐨𝐭𝐨𝐬
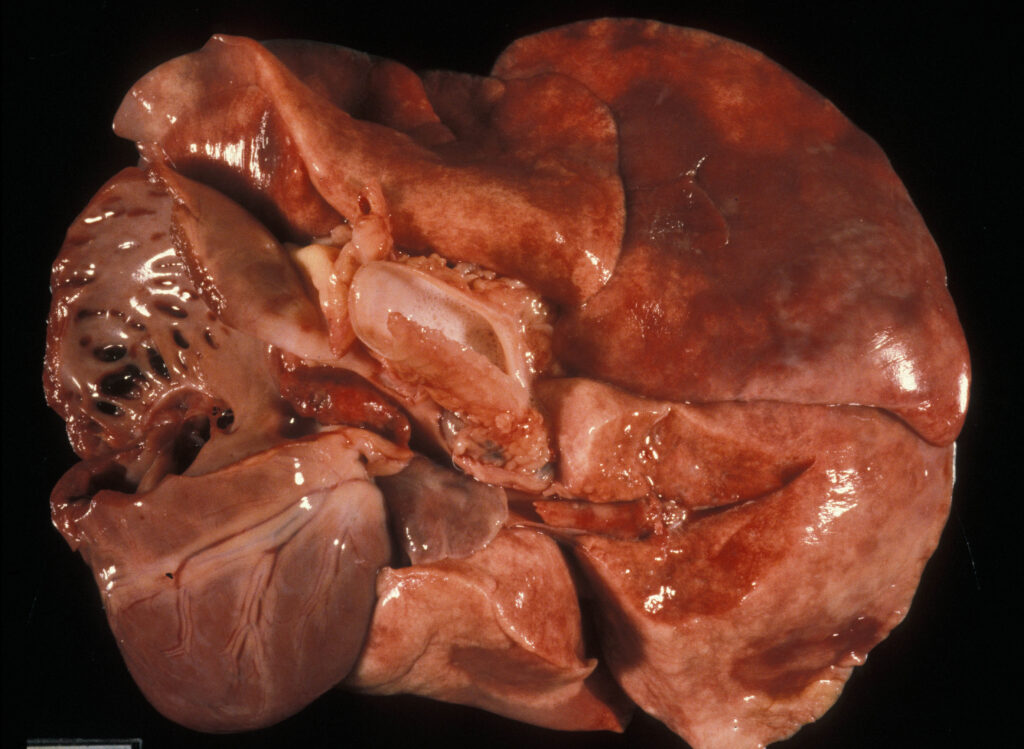
1) A pulmonary thrombus in a dog.
2) Two pulmonary thrombi in a cat, one going into each lung.
3) A pulmonary thrombus in a cow.
4) A cross-section of a horse lung showing the arteries blocked by a thrombus.
𝐒𝐨𝐮𝐫𝐜𝐞𝐬
Maxie, G. Jubb, Kennedy and Palmer’s Pathology of Domestic Animals, Volumes 2 and 3. Sixth Edition.
Photo 1-2 courtesy of Noah’s Arkive.
Photo 3-4 courtesy of University of Calgary Diagnostic Services Unit.