Today’s path rounds are on 𝐩𝐨𝐥𝐲𝐜𝐲𝐬𝐭𝐢𝐜 𝐤𝐢𝐝𝐧𝐞𝐲 𝐝𝐢𝐬𝐞𝐚𝐬𝐞!
𝐖𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭?
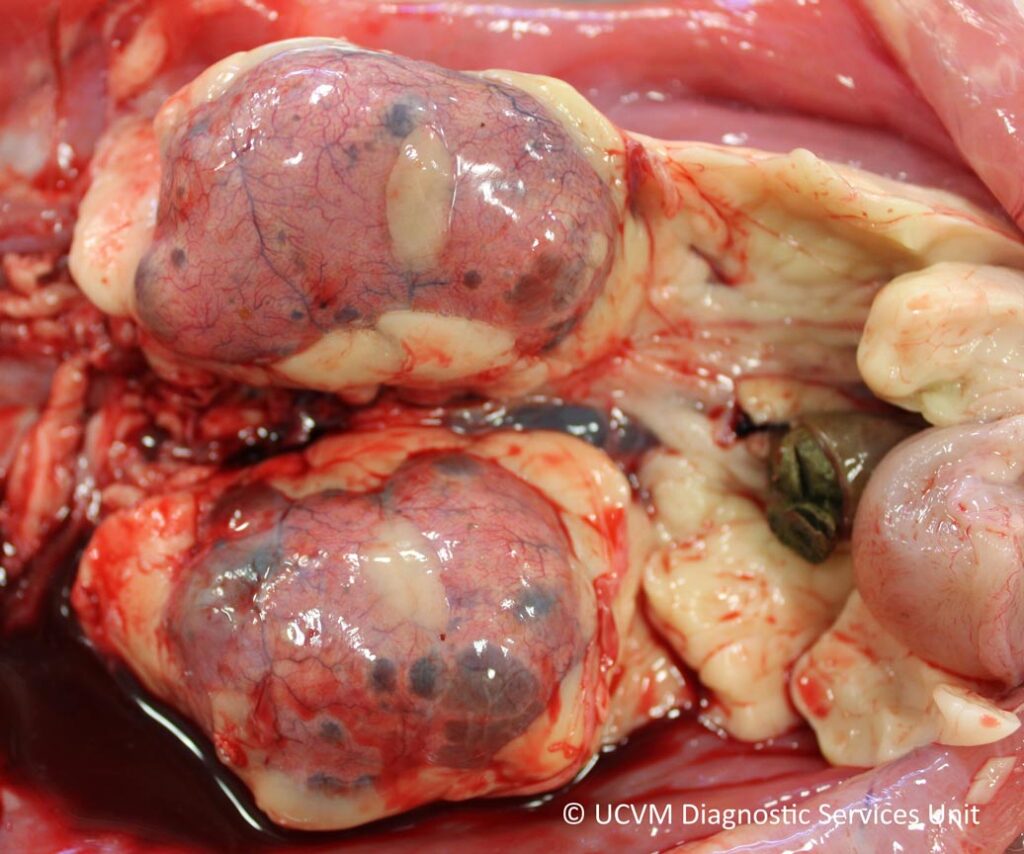
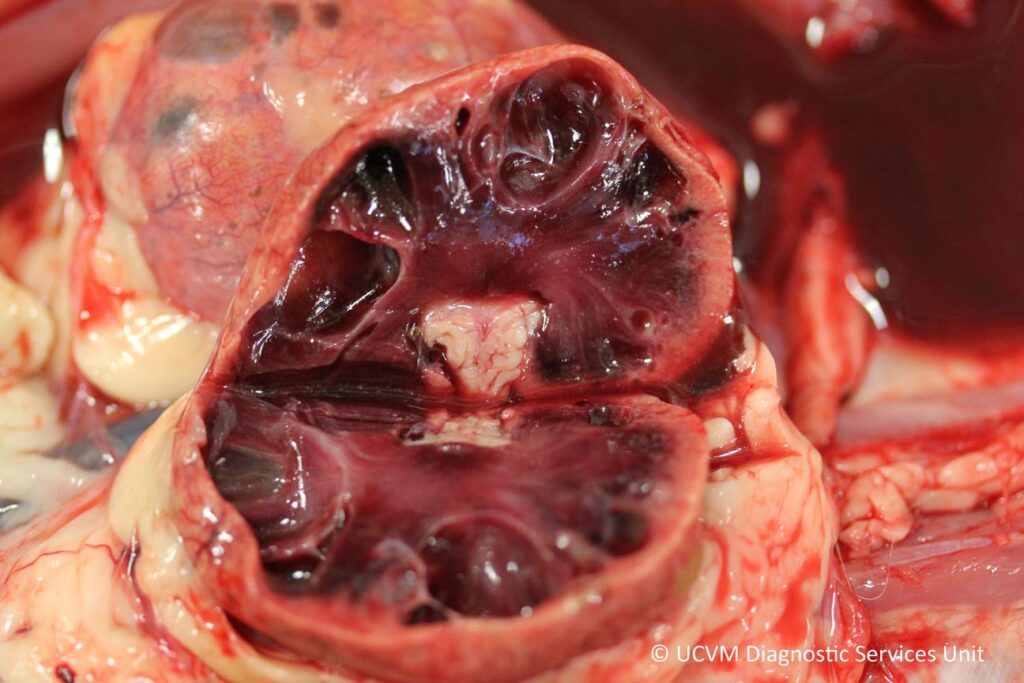
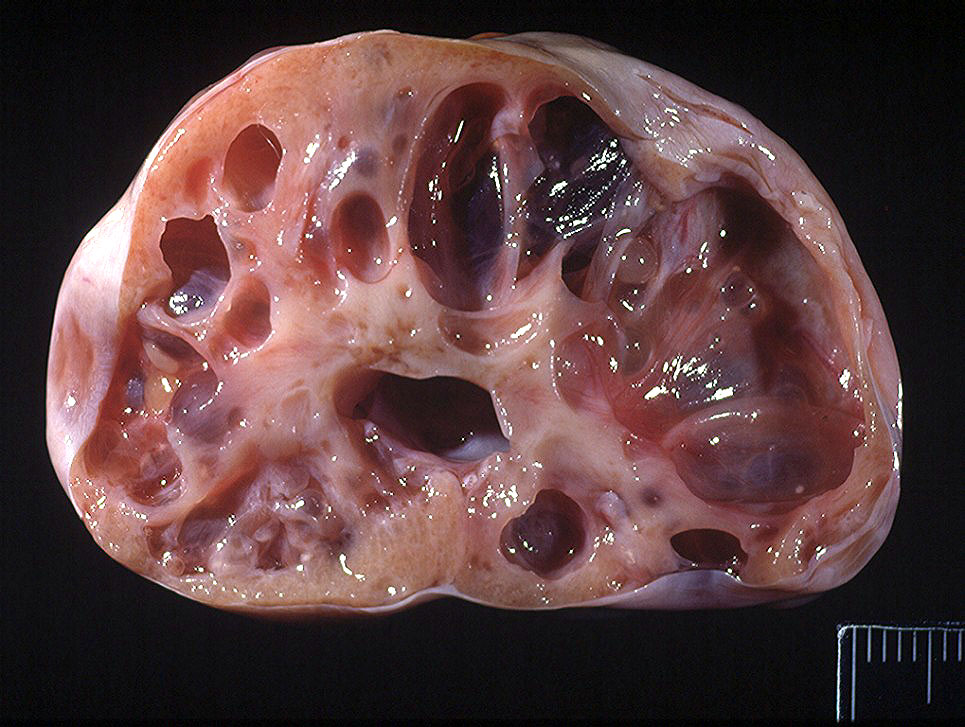
𝐏𝐨𝐥𝐲𝐜𝐲𝐬𝐭𝐢𝐜 𝐤𝐢𝐝𝐧𝐞𝐲 𝐝𝐢𝐬𝐞𝐚𝐬𝐞, or PKD, is an inherited disease of kidney development where multiple large 𝐜𝐲𝐬𝐭𝐬 (fluid filled structures with a lining) form within the kidney.
𝐖𝐡𝐨 𝐠𝐞𝐭𝐬 𝐢𝐭?
The typical “poster child” for this disease are Persian cats, however this disease has also been described in certain breeds of dogs and sheep. There have also been described cases of an unknown “origin” in piglets, calves, goats, puppies, kittens and foals.
𝐖𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐜𝐚𝐮𝐬𝐞𝐬 𝐢𝐭?
Generally, this disease is caused by genetic defects in the 𝐭𝐮𝐛𝐮𝐥𝐚𝐫 𝐞𝐩𝐢𝐭𝐡𝐞𝐥𝐢𝐚𝐥 𝐜𝐞𝐥𝐥𝐬 (cells that line the kidney tubules where urine is made). In particular, it is the 𝐜𝐢𝐥𝐢𝐚 (little projections of the cell into the tubule) that are affected, however it is not certain how their genetic abnormality leads to the development of cysts.
𝐖𝐡𝐲 𝐢𝐬 𝐭𝐡𝐢𝐬 𝐚 𝐩𝐫𝐨𝐛𝐥𝐞𝐦?
In general, small cysts or only a couple of cysts aren’t a huge issue, as the kidney has an amazing reserve capacity. In fact, you only see signs of renal failure once 70%+ of the kidney has been affected by a disease! However, these cysts tend to expand over time, causing compression of the normal kidney tissue around them, and ultimately death of those cells. So animals with PKD are particularly predisposed to renal failure as they age, due to the effect of these cysts.
𝐇𝐨𝐰 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭 𝐝𝐢𝐚𝐠𝐧𝐨𝐬𝐞𝐝?
PKD is generally diagnosed based on X-ray or ultrasound. You can also see signs of renal failure on bloodwork, if the animal has progressed to that stage.
𝐇𝐨𝐰 𝐢𝐬 𝐭𝐫𝐞𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐝?
Unfortunately the only real treatment is supportive care, as the kidneys themselves are fundamentally abnormal. Once these animals enter renal failure, their prognosis is often quite poor, leading to euthanasia.
𝐏𝐡𝐨𝐭𝐨𝐬
1-4) Some beautiful Swiss cheese kidneys ![]()
𝐒𝐨𝐮𝐫𝐜𝐞𝐬
Maxie, G. Jubb, Kennedy and Palmer’s Pathology of Domestic Animals, Volume 2. Sixth Edition.
Photos 1-2 courtesy of University of Calgary Diagnostic Services Unit.
Photos 3-4 courtesy of Noah’s Arkive.