Today’s path rounds are on 𝐏𝐚𝐫𝐚𝐬𝐜𝐚𝐫𝐢𝐬 𝐞𝐪𝐮𝐨𝐫𝐮𝐦!
𝐖𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭?
𝐏𝐚𝐫𝐚𝐬𝐜𝐚𝐫𝐢𝐬 𝐞𝐪𝐮𝐨𝐫𝐮𝐦 is a type of 𝐚𝐬𝐜𝐚𝐫𝐢𝐝, or roundworm, that affects the intestine of horses. These worms can get up to 50cm long!
𝐖𝐡𝐨 𝐠𝐞𝐭𝐬 𝐢𝐭?
This is most common in young horses, particularly foals and yearlings.
𝐇𝐨𝐰 𝐝𝐨 𝐚𝐧𝐢𝐦𝐚𝐥𝐬 𝐠𝐞𝐭 𝐢𝐧𝐟𝐞𝐜𝐭𝐞𝐝?
Parascaris has a 𝐝𝐢𝐫𝐞𝐜𝐭 𝐥𝐢𝐟𝐞𝐜𝐲𝐜𝐥𝐞, meaning that there are no other creatures involved in its transmission. Female worms in the intestine produce eggs, which are shed in the feces. Horses ingest feed contaminated with these eggs, which travels to the colon. In the colon, the eggs hatch into larvae which burrow into the colon wall and enter the blood stream. From there, the larvae migrate to the liver, then to the lungs, where they are coughed up and swallowed. When they reach the intestine, they mature and form adult worms.
𝐖𝐡𝐲 𝐢𝐬 𝐭𝐡𝐢𝐬 𝐚 𝐩𝐫𝐨𝐛𝐥𝐞𝐦?
One of the first issues with Parascaris is the fact the larvae migrate through the lungs. In the lungs, the movement of the larvae can cause multiple small hemorrhages and pneumonia. This can lead to coughing, secondary infections and other respiratory issues.
In the intestine, heavy worm burdens can completely or partially block the flow of intestinal contents through the gut. This can lead to reduced weight gain in forms, inappetence, colic, 𝐢𝐧𝐭𝐮𝐬𝐬𝐮𝐬𝐜𝐞𝐩𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 (telescoping of the intestine, see our previous post!) and in some cases even rupture of the intestine.
𝐇𝐨𝐰 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭 𝐝𝐢𝐚𝐠𝐧𝐨𝐬𝐞𝐝?
Ascarid infection can be diagnosed by a 𝐟𝐞𝐜𝐚𝐥 𝐟𝐥𝐨𝐚𝐭, where the number of ascarid eggs in the feces is counted. However, because you are only counting the eggs, this only tells the veterinarian about the number of female worms in the intestine, not the total population. To better appreciate the extent of infection, ultrasound is used to visualize the worms directly, and get a sense of how they are affecting the gastrointestinal tract.
𝐇𝐨𝐰 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭 𝐭𝐫𝐞𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐝? 𝐇𝐨𝐰 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭 𝐩𝐫𝐞𝐯𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐞𝐝?
If the foal is presenting with colic symptoms, treatment can either be done surgically to remove the worms, or with high doses of 𝐚𝐧𝐭𝐡𝐞𝐥𝐦𝐢𝐧𝐭𝐢𝐜𝐬 (dewormers). Routine fecal exams to look at numbers of eggs, and targeted deworming protocols, are the best bet for preventing these worm populations from getting out of control.
𝐏𝐡𝐨𝐭𝐨𝐬
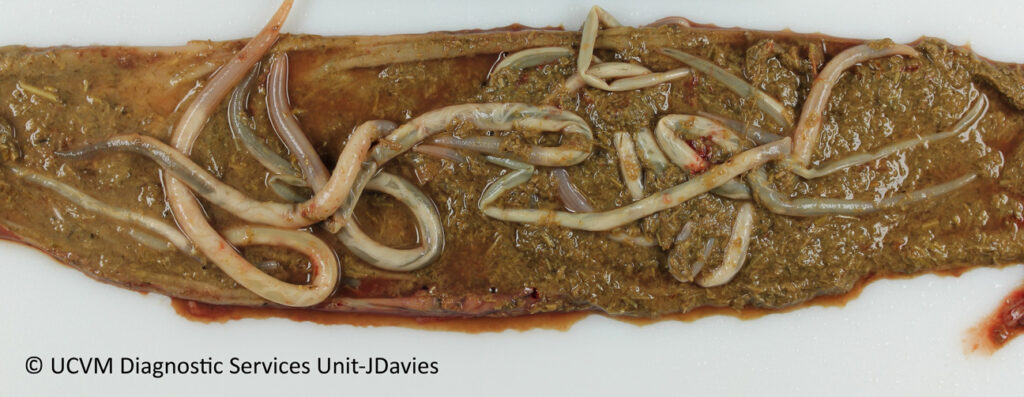
1-3) Examples of intestines with large numbers of ascarids inside.
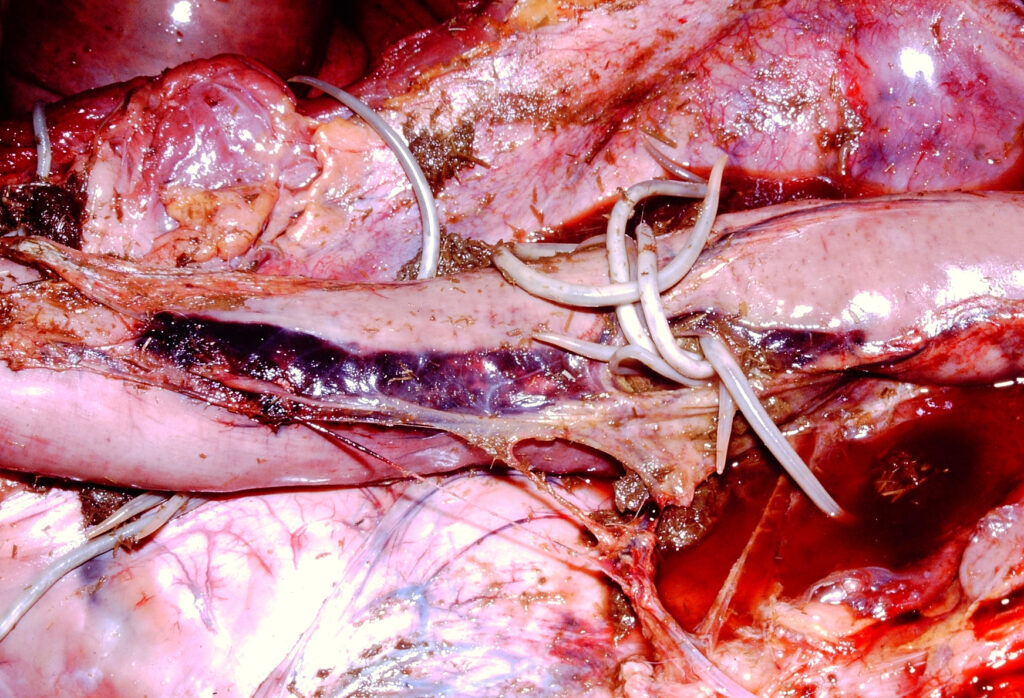
4) An example where the intestine ruptured due to the large number of ascarids.
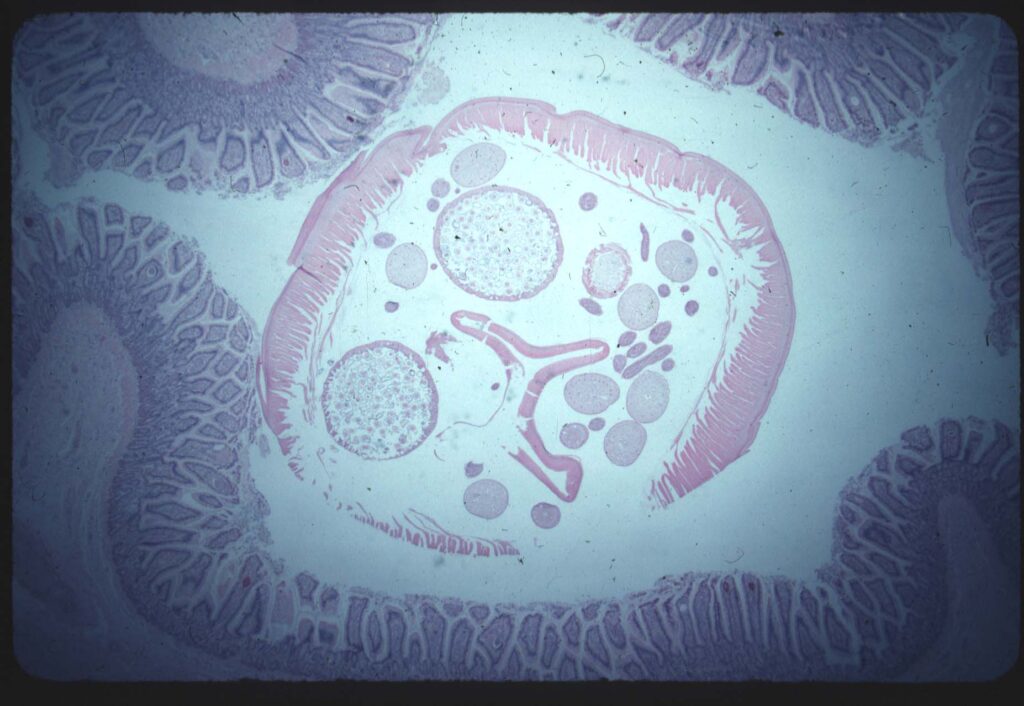
5) A cross-section of an ascarid on histology. They have organs just like animals do!
𝐒𝐨𝐮𝐫𝐜𝐞𝐬
Maxie, G. Jubb, Kennedy and Palmer’s Pathology of Domestic Animals, Volume 2. Sixth Edition.
Nielsen, M.K. Ascarid-associated colic in horses. Merck Veterinary Manual 2019.
Photos 1-3 courtesy of University of Calgary Diagnostic Services Unit.
Photos 4-5 courtesy of Noah’s Arkive.