Today’s path rounds are on the 𝐠𝐢𝐚𝐧𝐭 𝐤𝐢𝐝𝐧𝐞𝐲 𝐰𝐨𝐫𝐦, otherwise known as 𝐃𝐢𝐨𝐜𝐭𝐨𝐩𝐡𝐲𝐦𝐚 𝐫𝐞𝐧𝐚𝐥𝐞!
𝐖𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭?
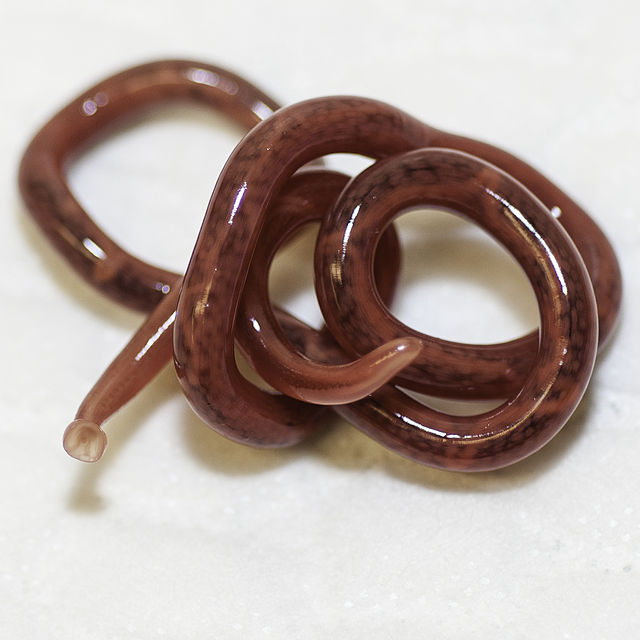
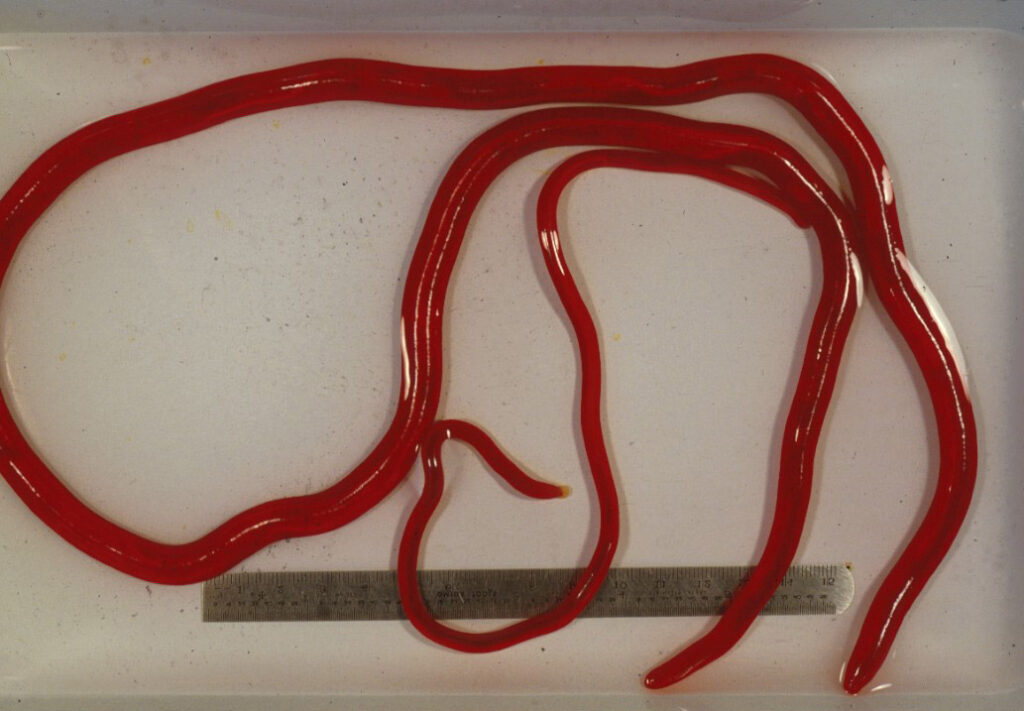
𝐃𝐢𝐨𝐜𝐭𝐨𝐩𝐡𝐲𝐦𝐚 𝐫𝐞𝐧𝐚𝐥𝐞 is the largest parasitic 𝐧𝐞𝐦𝐚𝐭𝐨𝐝𝐞 (roundworm) in our veterinary species. The female worms can measure up to 100cm long! As their name might suggest, they like to sit in and around the kidneys.
𝐖𝐡𝐨 𝐠𝐞𝐭𝐬 𝐢𝐭?
We most commonly see this disease in dogs and mink, but it can also be seen in other species.
𝐖𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐜𝐚𝐮𝐬𝐞𝐬 𝐢𝐭?
Dioctophyma has a life cycle involving two aquatic 𝐢𝐧𝐭𝐞𝐫𝐦𝐞𝐝𝐢𝐚𝐭𝐞 𝐡𝐨𝐬𝐭𝐬 which carry the larval stages of the worm. The worm’s eggs are shed in an infected animals urine, where they are picked up by “𝐦𝐮𝐝 𝐰𝐨𝐫𝐦𝐬“, which are basically like earthworms but live in the water. Here, they develop into their first larval stages. The infected mud worm is then eaten by a fish or frog, which allows the larvae to develop further. The infected fish or frog is then eaten by a mammal, like a dog or cat, and the larvae penetrate the intestinal wall and migrate towards the kidney. There they develop into the massive adults we can see at necropsy!
𝐖𝐡𝐲 𝐢𝐬 𝐭𝐡𝐢𝐬 𝐚 𝐩𝐫𝐨𝐛𝐥𝐞𝐦?
These giant worms take up a lot of space! In order to make space for themselves, they cause progressive destruction of the kidney 𝐩𝐚𝐫𝐞𝐧𝐜𝐡𝐲𝐦𝐚 (the tissue of the organ), until essentially all that remains is the 𝐫𝐞𝐧𝐚𝐥 𝐜𝐚𝐩𝐬𝐮𝐥𝐞 (covering of the kidney) with the worm inside. So as you might expect, these worms can cause all of the classic signs of kidney failure, as they are destroying one, or both, of the animal’s kidneys.
𝐇𝐨𝐰 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭 𝐝𝐢𝐚𝐠𝐧𝐨𝐬𝐞𝐝?
This disease is most easily diagnosed in the live patient by analyzing the 𝐮𝐫𝐢𝐧𝐞 𝐬𝐞𝐝𝐢𝐦𝐞𝐧𝐭, or what is left over after the water component of the urine is removed. Here, the veterinarian can see the eggs of Dioctophyma, which allows them to make the diagnosis.
𝐇𝐨𝐰 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭 𝐭𝐫𝐞𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐝? 𝐇𝐨𝐰 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭 𝐩𝐫𝐞𝐯𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐞𝐝?
The best treatment for this disease is complete removal of the affected kidney, particularly if only one kidney is affected. For prevention, keeping your pets from eating raw fish or other aquatic creatures is recommended!
𝐏𝐡𝐨𝐭𝐨𝐬
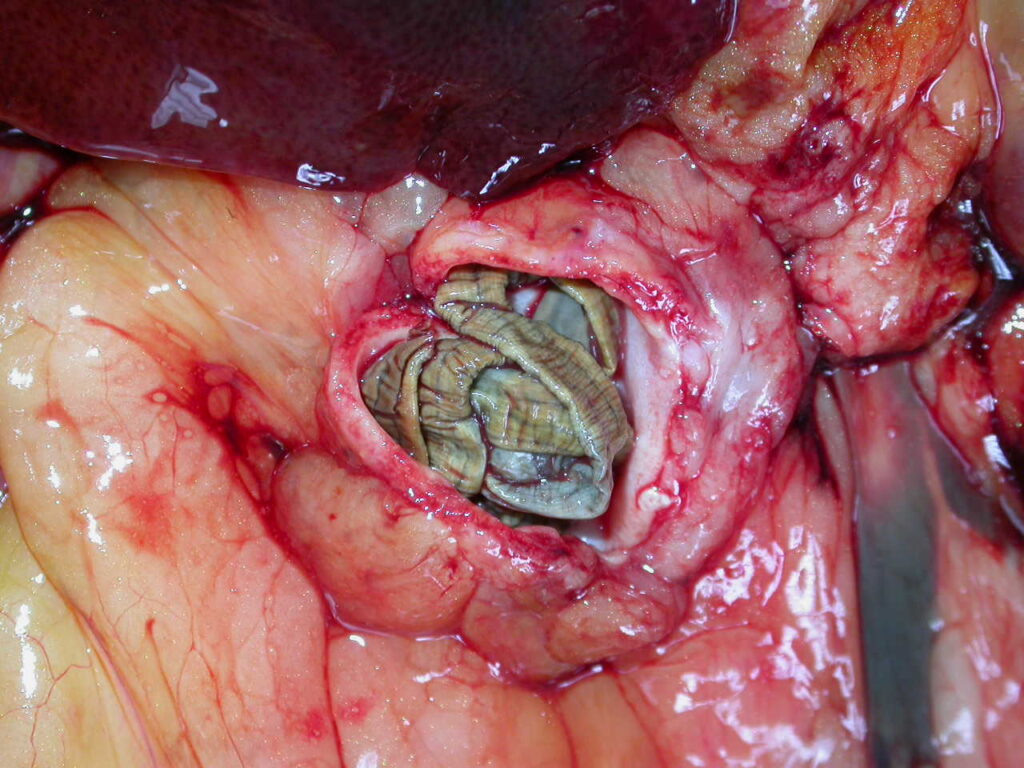
1-2) Two lovely examples of the adult female Dioctophyma after they were removed from an animal.
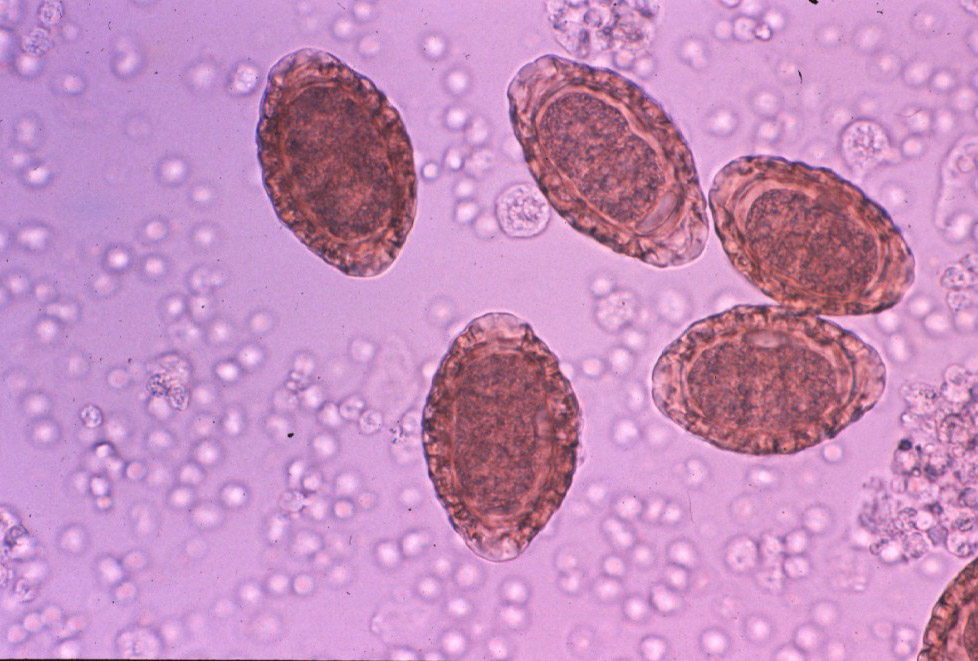
3) An example of the eggs of Dioctophyma on a urine sediment.
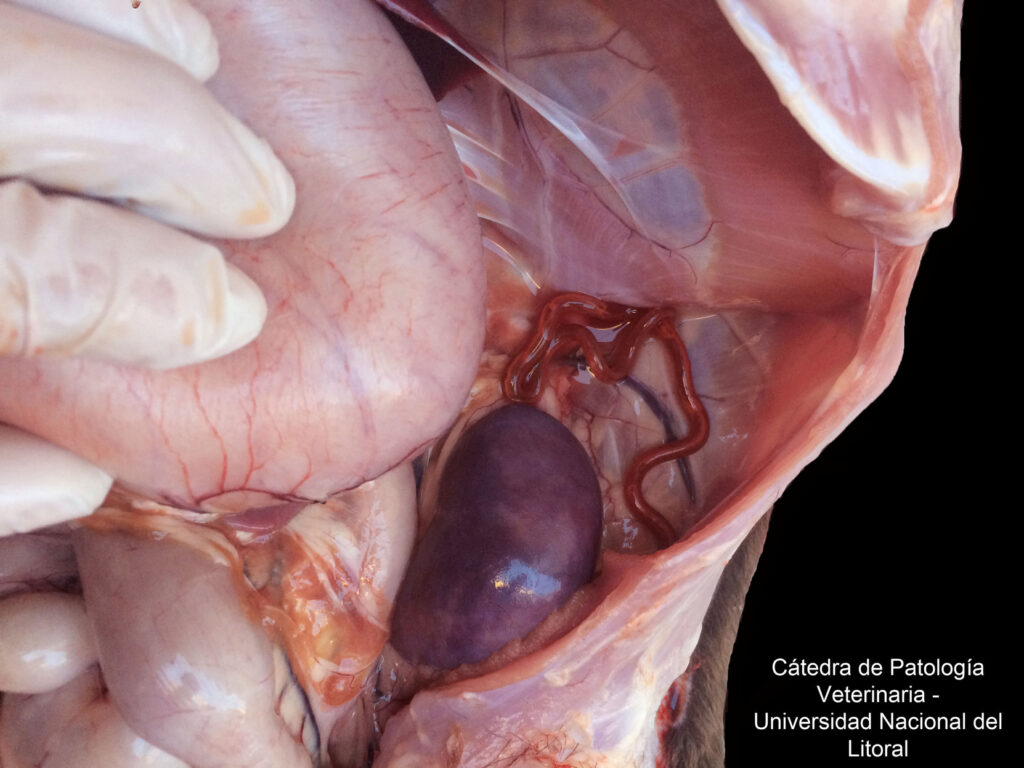
4-5) Two examples of dogs with Dioctophyma infections! Poor kidneys ![]()
𝐒𝐨𝐮𝐫𝐜𝐞𝐬
Maxie, G. Jubb, Kennedy and Palmer’s Pathology of Domestic Animals, Volume 2. Sixth Edition.
Brown, SA. Giant Kidney Worm Infection in Mink and Dogs. Merck Veterinary Manual 2015.
Photo 1 © Wikimedia Commons contributors Mandsager licensed under CC BY 3.0.
Photos 2-5 © Noah’s Arkive contributors Sacco-Canal, Prestwood, Barros, Barsanti licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0.