

Today’s path rounds are on 𝐥𝐲𝐦𝐩𝐡𝐨𝐦𝐚!
𝐖𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭?
𝐋𝐲𝐦𝐩𝐡𝐨𝐦𝐚 is a tumour of the 𝐥𝐲𝐦𝐩𝐡𝐨𝐜𝐲𝐭𝐞𝐬, one of the body’s major white blood cells. Because the white blood cells are found in the blood, these tumours can occur pretty much anywhere, and are always considered 𝐦𝐚𝐥𝐢𝐠𝐧𝐚𝐧𝐭 (aggressive).
𝐖𝐡𝐨 𝐠𝐞𝐭𝐬 𝐢𝐭?
Any species can get this!
𝐖𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐜𝐚𝐮𝐬𝐞𝐬 𝐢𝐭?
Just like basically every other cancer, the exact cause is often unknown. However, some species have particular viruses that can induce lymphomas, such as 𝐛𝐨𝐯𝐢𝐧𝐞 𝐥𝐞𝐮𝐤𝐨𝐬𝐢𝐬 𝐯𝐢𝐫𝐮𝐬 in cattle. In these species, testing for the virus can determine whether the lymphoma was 𝐞𝐧𝐳𝐨𝐨𝐭𝐢𝐜 (virus-induced) or spontaneously arose.
𝐖𝐡𝐲 𝐢𝐬 𝐭𝐡𝐢𝐬 𝐚 𝐩𝐫𝐨𝐛𝐥𝐞𝐦?
Because these tumours can occur virtually anywhere in the body, the clinical signs are highly variable. In general, organs where the virus sets up shop will have significantly decreased function. For example, lymphoma in the liver may lead to liver failure, or lymphoma in the eye may cause blindness. Dealing with large tumours generally makes the animal feel pretty dumpy, so they often have weight loss, lethargy and weakness as well.
𝐇𝐨𝐰 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭 𝐝𝐢𝐚𝐠𝐧𝐨𝐬𝐞𝐝?
Identifying the location of the tumours can be done via physical examination, ultrasound or X-rays. From there, confirming the type of tumour is important. Usually, this is done by either 𝐜𝐲𝐭𝐨𝐥𝐨𝐠𝐲, where a sample of cells is taken by a needle and examined under the microscope, or 𝐡𝐢𝐬𝐭𝐨𝐩𝐚𝐭𝐡𝐨𝐥𝐨𝐠𝐲, where a piece of the tumour is removed and examined. In both cases, the pathologist will see a large number of strange looking lymphocytes, confirming the diagnosis.
𝐇𝐨𝐰 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭 𝐭𝐫𝐞𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐝?
Thankfully, lymphomas are quite responsive to 𝐜𝐡𝐞𝐦𝐨𝐭𝐡𝐞𝐫𝐚𝐩𝐲, where specific drugs are used to target the tumour. Radiation therapy can also be used to improve success. In fact, it is estimated that over 90% of dogs will achieve complete remission!
𝐏𝐡𝐨𝐭𝐨𝐬
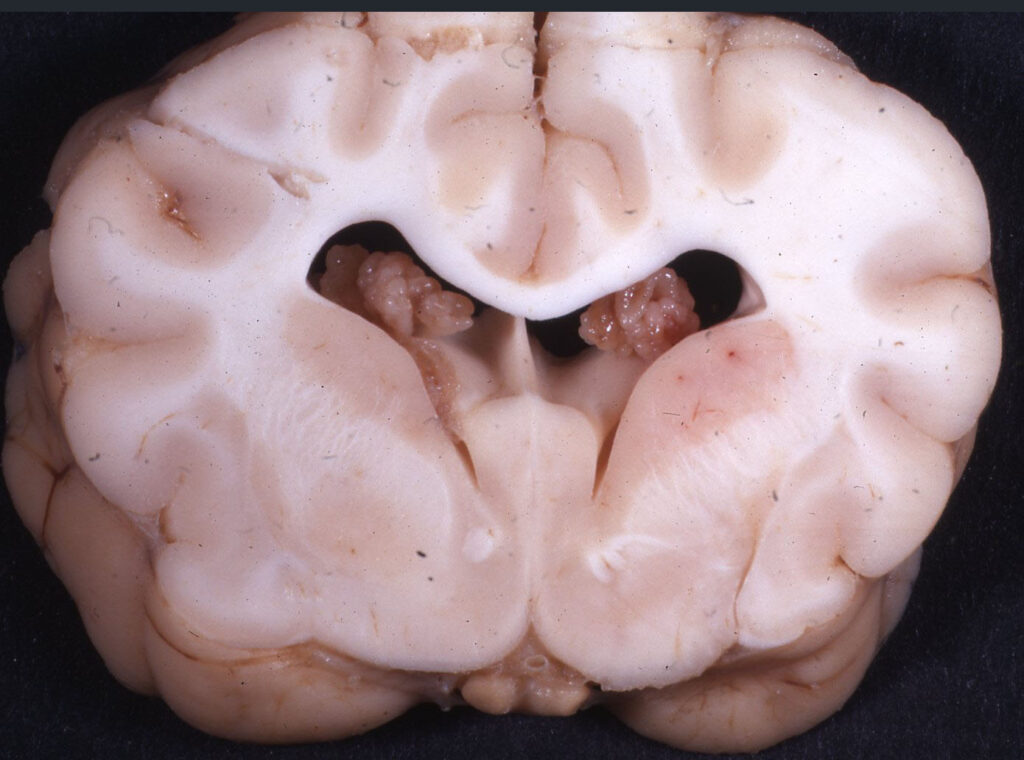
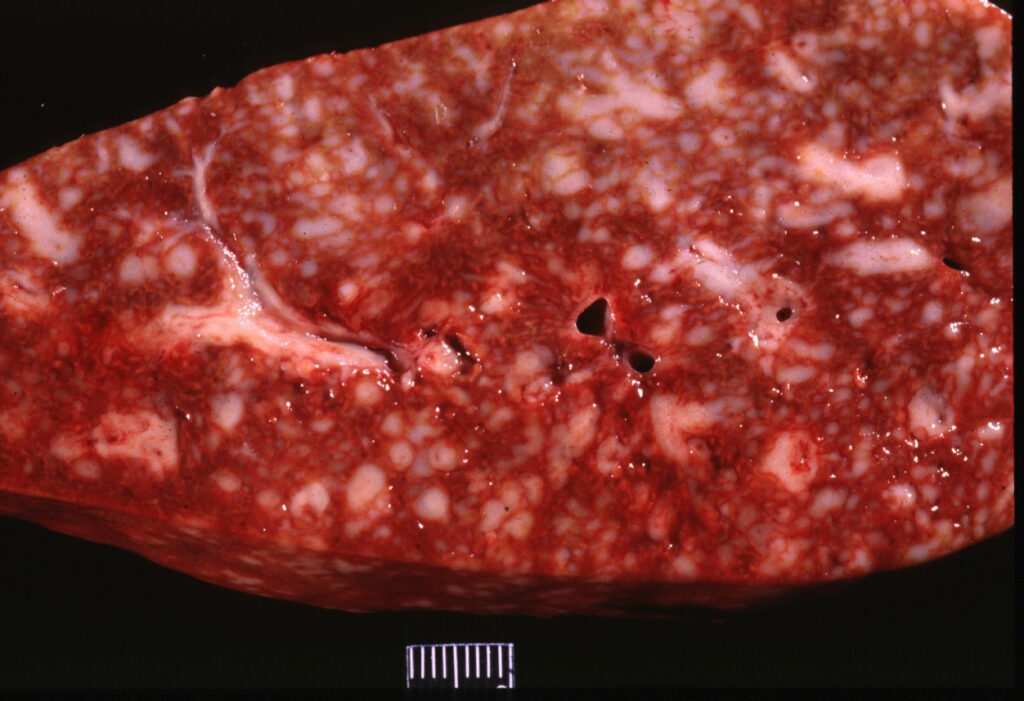
1-6) Organs with lymphoma! In order: spleen, liver, lung, brain, eye and bone marrow. Note how the tumour tissue is quite white… it is made of white blood cells after all!
7) A cytology from lymphoma showing a bunch of big lymphocytes!
𝐒𝐨𝐮𝐫𝐜𝐞𝐬
Maxie, G. Jubb, Kennedy and Palmer’s Pathology of Domestic Animals, Volume 3. Sixth Edition.
Photos 1 and 6 © University of Calgary Diagnostic Services Unit.
Photos 2-5, 7 © Noah’s Arkive contributors Jakowski, Sagartz, Young licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0.