Today’s path rounds are on 𝐜𝐚𝐧𝐝𝐢𝐝𝐢𝐚𝐬𝐢𝐬, also known as 𝐭𝐡𝐫𝐮𝐬𝐡!
𝐖𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭?
𝐂𝐚𝐧𝐝𝐢𝐝𝐢𝐚𝐬𝐢𝐬 is an infection with 𝐂𝐚𝐧𝐝𝐢𝐝𝐚, a fungus that is normally found in the mouth and gastrointestinal tract of animals. Under certain circumstances, this fungus can proliferate, causing the disease!
𝐖𝐡𝐨 𝐠𝐞𝐭𝐬 𝐢𝐭?
This disease can be seen in any species! However, it is mainly seen in young animals, like foals and calves, especially ones that have received antibiotics.
𝐖𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐜𝐚𝐮𝐬𝐞𝐬 𝐢𝐭?
When there is a change in the normal 𝐦𝐮𝐜𝐨𝐬𝐚𝐥 𝐟𝐥𝐨𝐫𝐚 (the bacteria and fungi that live in the gastrointestinal tract), Candida may be allowed to grow more than it normally would. This typically occurs after antibiotics are given to the animal, which kill off a large number of the normal bacteria in the gut, allowing Candida access to more nutrients. However, stress or other immune suppressive conditions can also allow this change to occur.
𝐖𝐡𝐲 𝐢𝐬 𝐭𝐡𝐢𝐬 𝐚 𝐩𝐫𝐨𝐛𝐥𝐞𝐦?
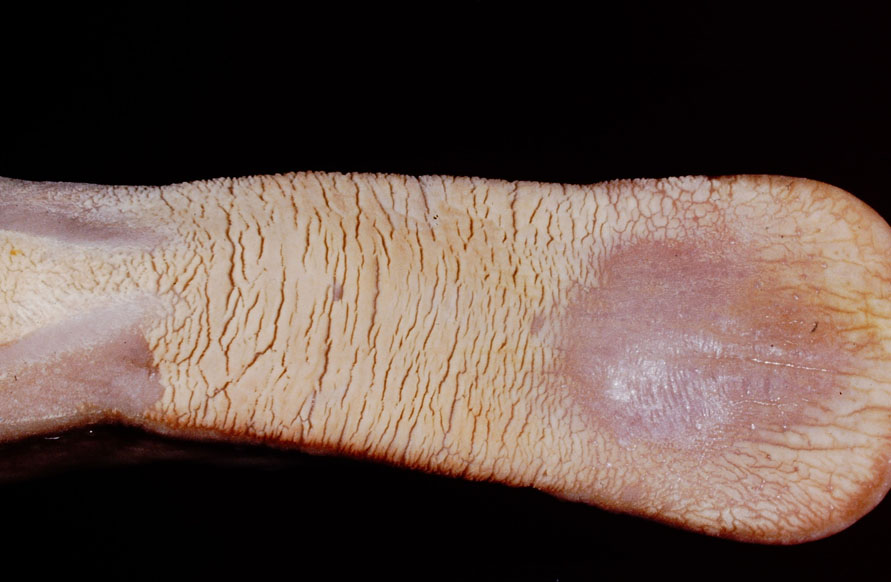
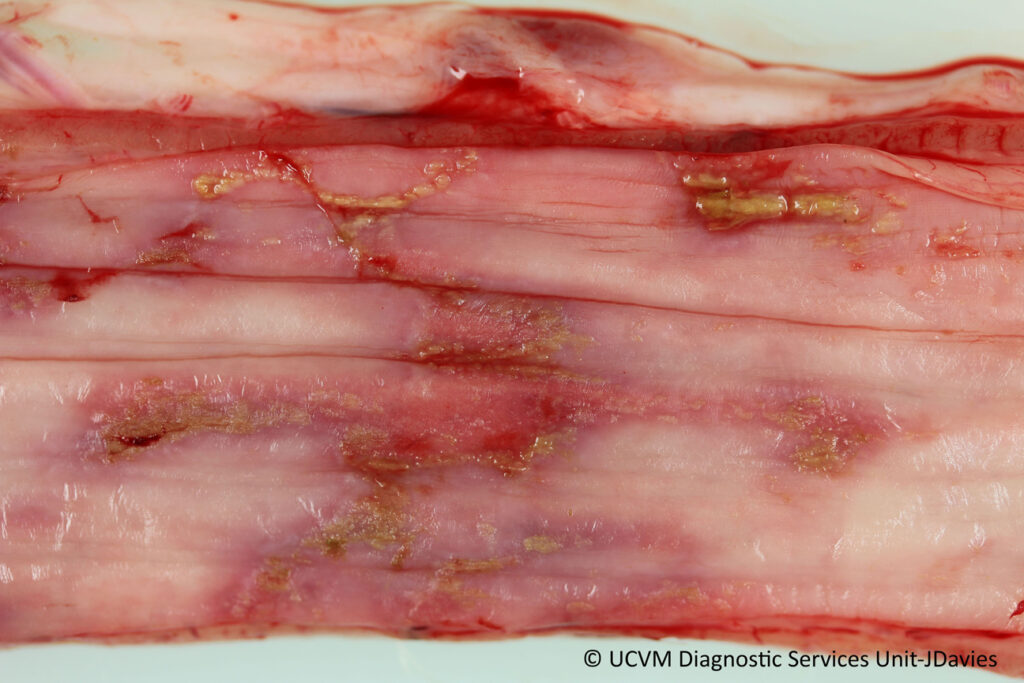
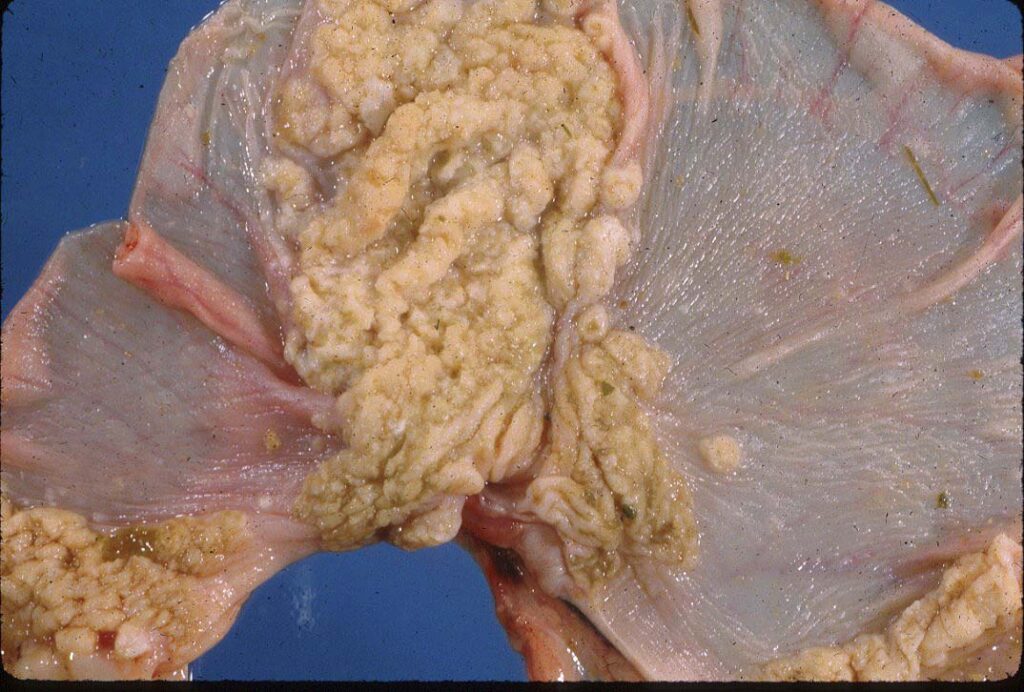
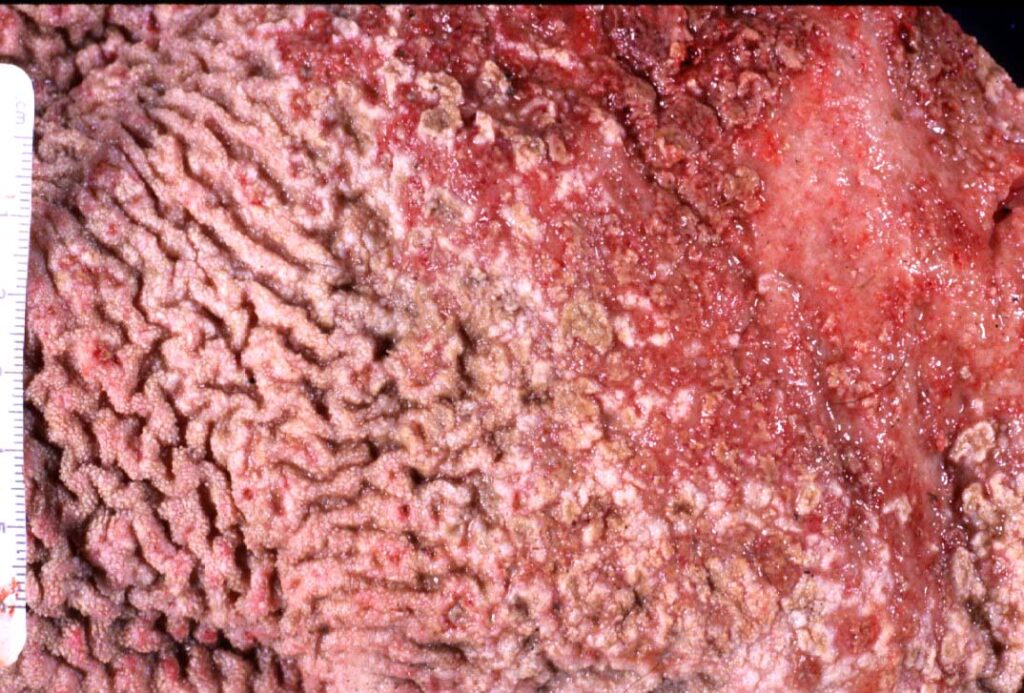
When Candida proliferates, it attaches itself to the 𝐞𝐩𝐢𝐭𝐡𝐞𝐥𝐢𝐮𝐦 (cells lining the gut) and can release enzymes that cause damage to the cells. The fungus’ yeast forms will continue to accumulate, eventually producing a plaque-like mass on the gut surface. We most commonly see this on the tongue, but it can also be seen in the esophagus and stomach or rumen. The damage to the epithelium can lead to 𝐮𝐥𝐜𝐞𝐫𝐬 (erosions in the gut surface) that can be very painful, and potentially give the fungus access to the bloodstream where it can spread to other organs.
𝐇𝐨𝐰 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭 𝐝𝐢𝐚𝐠𝐧𝐨𝐬𝐞𝐝?
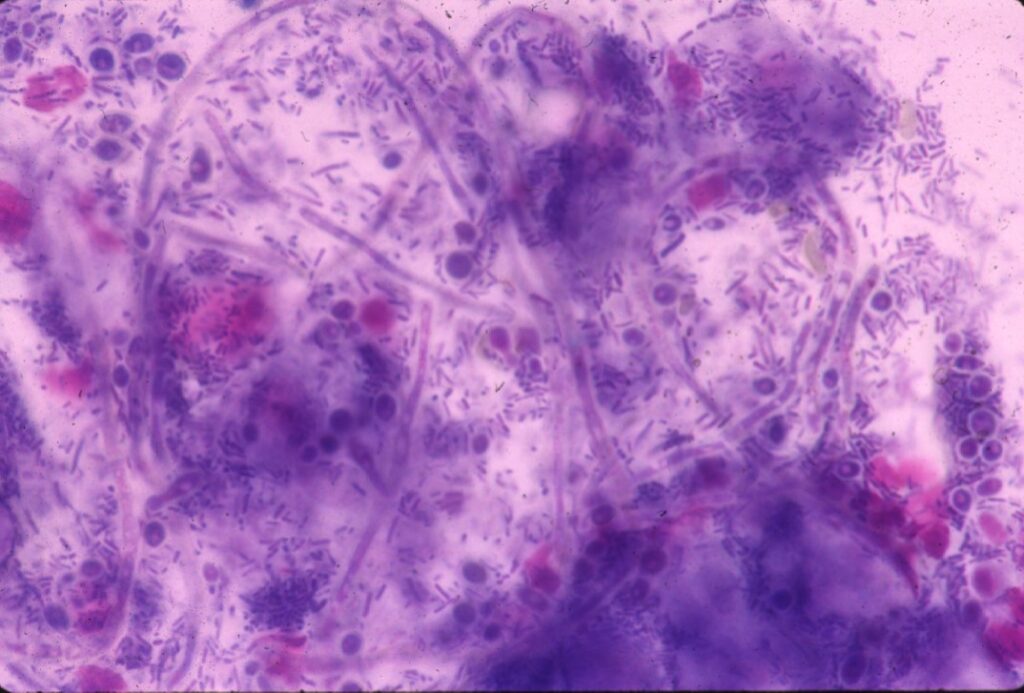
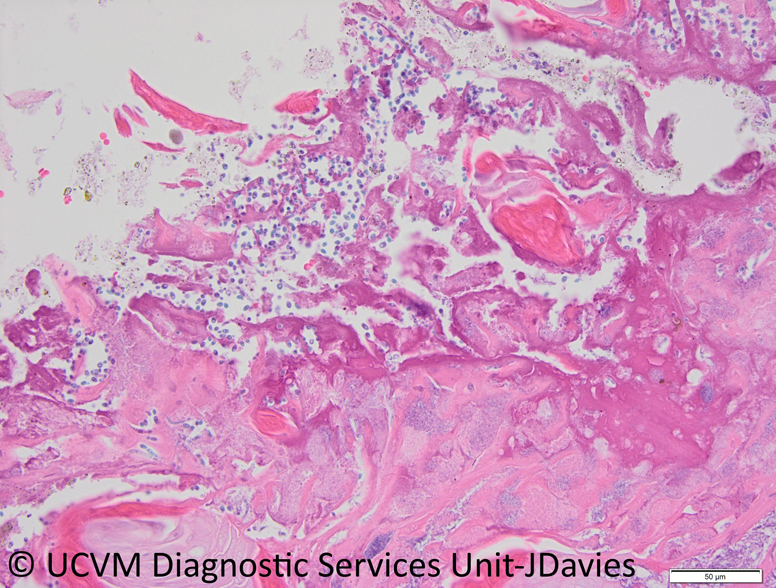
Candida can easily be identified on 𝐬𝐜𝐫𝐚𝐩𝐢𝐧𝐠𝐬 of the thick tissue on the gut surface, or from 𝐛𝐢𝐨𝐩𝐬𝐢𝐞𝐬. They look like little ovals with a thin cell wall, that often form long chains.
𝐇𝐨𝐰 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭 𝐭𝐫𝐞𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐝?
Thankfully, Candida is quite susceptible to our typical antifungals. However, it is important to remember that the proliferation occurred due to some change in the gut flora, so identifying and correcting that issue is often critical in a successful treatment plan!
𝐏𝐡𝐨𝐭𝐨𝐬
1-4) Examples of Candida on a tongue, esophagus, stomach and rumen!
5) Candida as shown in a scraping of one of the fungal plaques.
6) Candida in a biopsy from the mouth!
𝐒𝐨𝐮𝐫𝐜𝐞𝐬
Maxie, G. Jubb, Kennedy and Palmer’s Pathology of Domestic Animals, Volume 2. Sixth Edition.
Taboada J. Candidiasis. Merck Veterinary Manual 2020.
Photos 1-3, 5 © Noah’s Arkive contributors McNamara, Acland, Harrington, Lowenstine licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0.
Photos 4 and 6 © University of Calgary Diagnostic Services Unit.